40m+3×50m非对称预应力混凝土连续箱梁桥设计(含CAD图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
40m+3×50m非对称预应力混凝土连续箱梁桥设计(含CAD图)(任务书,开题报告,论文说明书19000字,CAD图28张)
摘要
预应力混凝土连续梁桥具有整体性能好、结构刚度大、变形小、抗震性能有利于高速行车等优点。另外箱型截面具有良好的抗弯抗扭性能、便于养护等优点。目前,国内预应力施工技术也到达炉火纯青的地步。
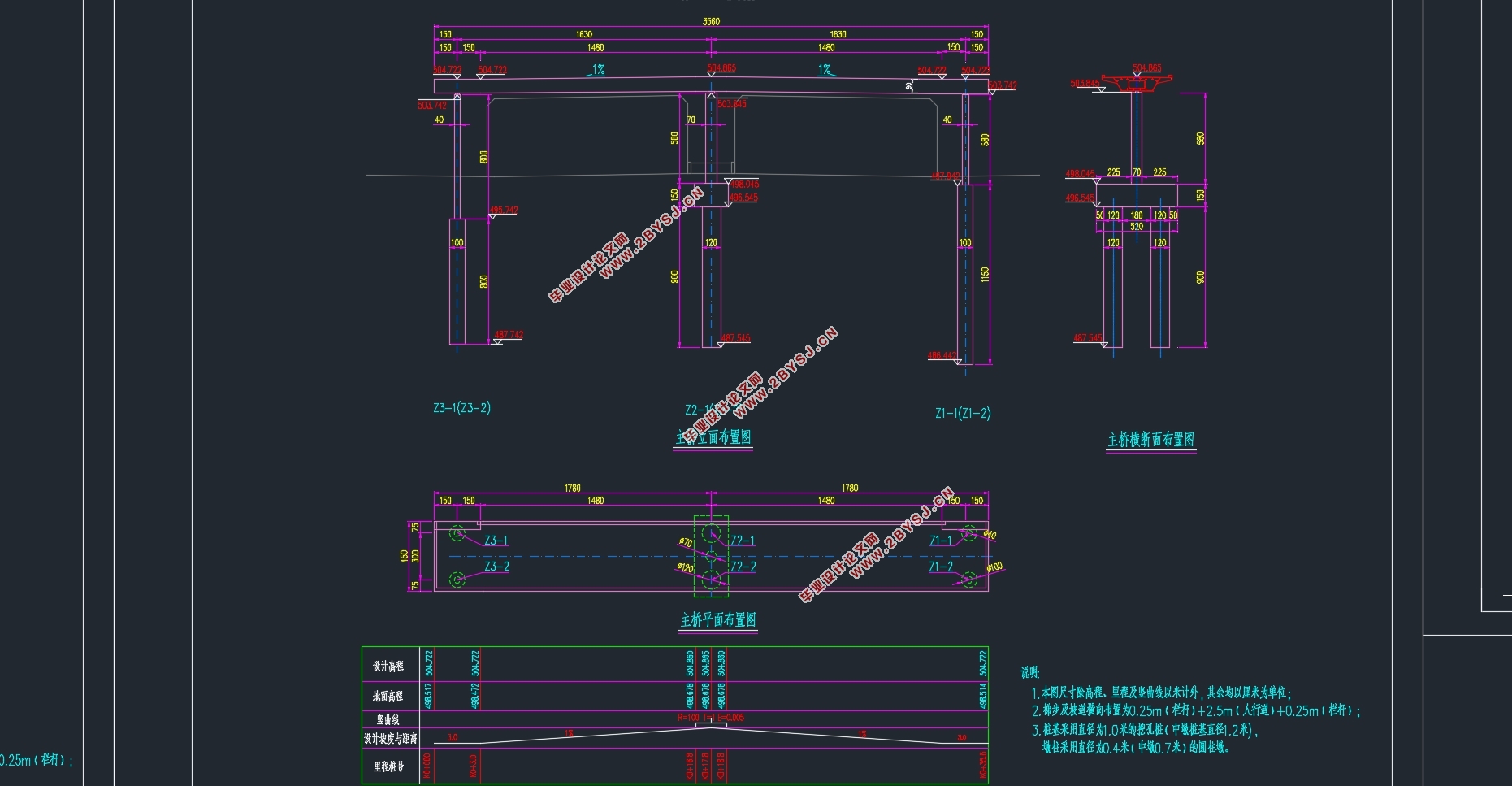
本次毕业设计采用40m+3×50m的非对称预应力混凝土等截面连续箱梁的形式,梁宽14m,梁高2.8m。荷载等级为公路I级。横断面采用单箱单室截面,其中跨中顶底板厚度均为25cm,腹板厚度均为50cm。根据受力需要在支点附近顶板、底板、腹板厚度会有变化。本次设计主梁采用满堂支架法施工,用midas/civil软件建立全桥有限元模型,进行上部结构配筋设计和内力计算。下部结构的设计和计算包括墩柱的设计与计算以及桩基基础的设计与计算。
通过这次设计,掌握了midas软件的基本操作和桥梁结构设计的基本理论,提高分析解决实际问题的能力。
关键词:预应力混凝土连续梁桥、箱梁、结构分析、配筋设计
Abstract
Prestressed concrete continuous girder bridge has the advantages of good overall performance, large structural rigidity, small deformation, good seismic performance and temperature adaptability, and is advantageous for high speed driving. In addition, the box section has good bending and torsional resistance, small deformation, easy to maintain and so on. At present, the domestic prestressed construction technology also reached the point of perfection.
The graduation design uses 40m +3 × 50m asymmetric prestressed concrete and other sections of the form of continuous box girder, beam width 14m, beam height 2.8m. The load rating is Highway I. Cross-section with single-box single-chamber section, which across the top and bottom plate thickness of 25cm, web thickness of 50cm. According to the force required in the vicinity of the fulcrum roof, floor, web thickness will change. The design of the main beam using full-frame construction method, with midas / civil software to build full-bridge finite element model, the upper structure of the reinforcement design and internal force calculation. The design and calculation of the lower structure includes the design and calculation of the pier and the design and calculation of the pile foundation.
Through this design, master the basic operation of midas software and bridge structure design of the basic theory, improve the ability to analyze and solve practical problems
Keywords :Prestressed concrete continuous girder bridge, box girder, structural analysis, reinforcement design



目录
1.绪论 1
1.1 预应力混凝土连续箱梁桥概述 1
1.2毕业设计的目的和意义 1
1.2.1 毕业设计的目的 1
1.2.2 毕业设计的意义 2
2.结构初步设计 3
2.1 设计概述 3
2.2 设计基础资料 3
2.3 技术标准与设计规范 3
2.4 主要材料 3
2.4.1 混凝土 3
2.4.2 钢材 4
2.4.3 支座伸缩缝 4
2.4.4其他材料 4
2.5 截面尺寸拟定 4
2.5.1 等截面箱梁的形式 4
2.6 施工方法 7
3.40+3×50m等截面连续箱梁桥Midas模型建立 8
3.1 设定模型操作环境 8
3.2 定义材料 8
3.3 建立截面 10
3.3.1 建立单元与节点 10
3.3.2 导入截面 11
3.3.3 定义变截面和变截面组 13
3.4 全桥模型 14
3.5 定义时间依存特性 15
3.6 定义边界条件 16
3.7 定义静力荷载工况 16
3.8 定义移动荷载工况 18
3.9 定义支座沉降 20
3.10定义施工阶段 21
4.主梁内力计算 23
4.1 生成荷载组合 23
4.2 恒载内力计算 23
4.2.1 一期恒载内力计算 23
4.2.2 二期恒载内力计算 27
4.3 活载内力计算 30
5.钢筋的估算与布置 35
5.1 预应力钢束的估算与布置 35
5.1.1 预应力钢束估算 35
Ra—混凝土抗压设计强度; 36
(2)按正常使用极限状态计算 36
5.1.2 预应力钢束估算结果 38
5.1.3 纵向预应力钢束的布置 43
5.1.4 输入预应力钢筋 44
5.2 普通钢筋的估算与布置 46
5.2.1 普通钢筋布置原则 46
5.2.2 普通钢筋的输入 47
6.预应力损失及有效预应力计算 49
6.1 预应力钢筋与管道之间的摩擦损失 49
6.2 锚具变形、钢筋回缩和接缝压缩产生的预应力损失 49
6.3 混凝土弹性压缩产生的预应力损失 50
6.4 预应力钢筋应力松弛产生的预应力损失 50
6.5 混凝土的收缩和徐变产生的预应力损失 50
6.6 有效预应力计算 52
7.次内力计算 61
7.1 徐变次内力 61
7.2 收缩次内力 64
7.3 预加力引起的次内力 66
7.4 温度次内力 69
7.5 支座不均匀沉降引起的次内力 72
8 截面验算 76
8.1 使用阶段正截面抗弯验算 76
8.2 施工阶段法向压应力验算 77
8.3 使用阶段正截面压应力验算 79
8.4 受拉区钢筋的拉应力验算 81
8.5 使用阶段正截面抗裂验算 86
9.墩柱的设计与计算 89
9.1 截面尺寸拟定 89
9.2截面配筋计算及应力验算 90
9.2.1 作用于墩柱顶的外力 90
9.2.2 作用于墩柱底外力 90
9.3.2 截面配筋计算 90
10.钻孔灌注桩计算 93
10.1 荷载计算 93
10.2 桩长计算 93
10.3 桩基配筋计算及桩身材料截面强度验算 95
结束语 98
参考文献 99
致谢 101
