无线防盗报警器设计
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
无线防盗报警器设计(任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文12000字)
摘 要
本课题主要是在AT89S52单片机的基础上利用无线通信技术和传感器技术,设计出能够实现检测人体红外信号和振动信号的报警装置。装置具备可人为控制的布防、撤防、测试功能。红外检测模块、振动监控模块和主控报警电路之间通过无线装置进行连接。布防之后主人有一定的时间可以离开报警装置,防止误报警。布防后无人靠近或者没有任何振动的时候报警装置处于警备状态。当有人闯入布防区或者震动检测装置检测到震动源进入到防盗装置的时候,装置处于报警状态,进行声光报警。在报警的同时显示出报警位置,如果两路都在报警的情况下,则以最后一个触动报警装置的为准。报警的时候可以通过主控电路撤防或者使用无线遥控器撤防使装置不再报警。
本文在研究完无线防盗报警装置的国内外研究概况之后,对装置的硬件和软件进行设计、仿真测试与制作。经过测试,电路工作稳定、能够完整实现预定功能。
关键词:无线 防盗 报警
Wireless Burglar Alarm Design
ABSTRACT
This paper is mainly based on the SCT89S52 microcontroller using wireless communication technology and sensor technology, designed to enable detection of human infrared signal and a vibration signal of alarm. Apparatus includes a human-controlled arm, disarm, test function. Infrared detection module, between the vibrating alarm monitoring module and the main control circuit connected via wireless devices. After a certain time arming the owner can leave the alarm device to prevent false alarms. After arming unmanned near or when no vibration alarm device is on alert. When someone broke into armed zone or vibration detection means detects the vibration source into the anti-theft device when the device is in alarm state, sound and light alarm. While the alarm shows the alarm location, in the case if the two are in alarm, the last found a subject touched alarm device. When the alarm can be disarmed by the control circuit or by using a wireless remote control of the device is no longer disarm the alarm.
Based on the study after study completed abroad before wireless burglar alarm devices, hardware and software device design, simulation testing and production. After testing, the circuit is stable, can fully realize the predetermined function.

目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
目录 III
第一章 导论 1
1.1 背景及意义 1
1.2 相关发展现状 2
1.3 设计要求 4
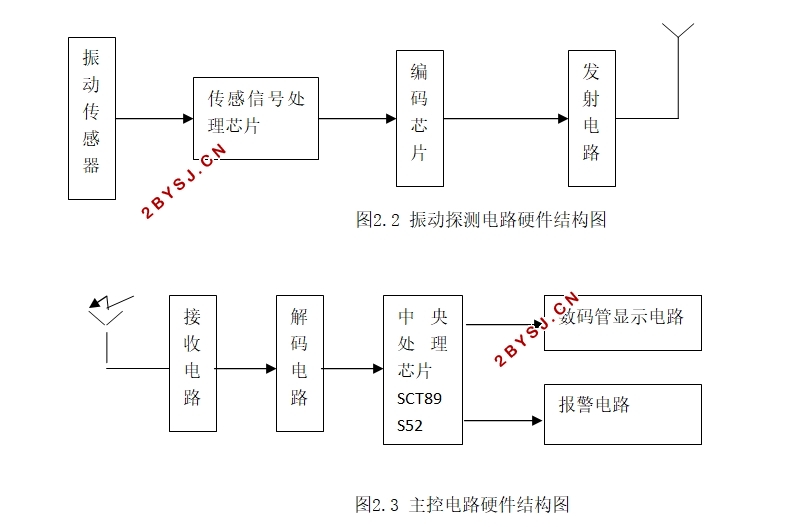
第二章 报警器硬件设计 6
2.1 设计思路 6
2.2 人体红外热释检测模块 8
2.3 振动检测模块 10
2.4 主控系统 12
2.4.1单片机最小系统 12
2.4.2接收电路 14
2.4.3报警显示电路 15
2.5 遥控器电路设计 15
2.6 整体电路 16
第三章 软件设计 18
3.1主程序设计流程 18
3.2对主程序进行设计 19
3.3程序调试 22
3.4 系统仿真 23
第四章 成品制作与测试 25
4.1 硬件焊接 25
4.2 功能测试 26
第六章 总结与展望 27
参考文献 28
致谢 29
