基于单片机的语音存储与回放装置设计
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
基于单片机的语音存储与回放装置设计(任务书,开题报告,论文12000字)
摘要
本设计采用AT89C51单片机控制芯片、ISD4004语音芯片和LM386集成功率集放大器芯片设计一款语音录放存储系统,能够实现单次录音时间长达达8分钟、录音放音切换、放音片段的选取受按键控制,可复位等功能。
有三个模块在整个系统:51单片机控制模块,语音芯片录放模块和功率放大模块。系统控制模块的核心是51单片微型计算机的控制功能。语音记录和回放模块的操作模式是由识别的按键的控制;语音记录和回放模块可实现处理的功能,存储和恢复的声音;功率放大器模块可申请恢复的音频信号放大,使声音更清晰,更明亮。整体解决方案的设计,硬件电路设计和软件设计:整个设计在这三个方面研究。
关键词:控制芯片 语音芯片 语音存储 语音回放。
Abstract
This design USES AT89C51 single-chip microcomputer control chip, ISD4004 voice chip and LM386 integrated power set amplifier chip to design a voice recording and storage system, which can achieve a single recording time up to 8 minutes long, recording and playback switch, playback clip selection by button control, reset and other functions.
There are three modules in the whole system: 51 MCU control module, voice chip recording and playback module, and power amplifier module. The core of system control module is 51 single chip microcomputer control function. The operation mode of the voice recording and playback module is controlled by the recognized keys. Voice recording and playback module can achieve the function of processing, storage and recovery of sound; The power amplifier module can be applied to recover the audio signal amplification, making the sound clearer and brighter. Overall solution design, hardware circuit design and software design: the whole design in three aspects.
Key words: control chip voice chip voice storage voice playback

目录
摘要••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••I
Abstract••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••II
第一章.绪论•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••1
1.1 课题研究背景及科学意义•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••1
1.2 国内外研究现状•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••2
1.3 发展前景••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••2
1.4 设计任务与要求•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••3
第二章.总体方案设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4
2.1 系统原理••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4
2.2 器件选择•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4
2.2.1 单片机的选择••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4
2.2.2 语音芯片选择••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••5
2.2.3 功放选择••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••5
2.2.4 液晶显示屏选择•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••5
2.3 各芯片详细说明••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••5
2.3.1 AT89C51芯片•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••5
2.3.2 ISD4004语音芯片••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••9
2.3.3 LM386芯片•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••11
2.3.4 1602液晶显示屏•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••13
第三章.硬件电路设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••15
3.1 电源•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••15
3.2 51单片机最小系统电路•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••15
3.3语音电路设计•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••16
3.4功放电路设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••16
3.5按键电路设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••17
3.6指示灯电路设计•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••18
3.7 LCD1602液晶显示电路•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••19
第四章.软件设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••20
4.1程序编写环境•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••20
4.2主程序工作原理及流程图••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••20
4.3子程序工作原理及流程图•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••21
4.3.1录音子程序•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••21
4.3.2 放音子程序••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••22
第五章.系统调试与实验结果•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••23
5.1系统调试••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••23
5.1.1 按照画好的硬件电路设计图焊接好实物••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••23
5.1.2将程序烧写进单片机••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••24
5.1.3接通电源进行调试••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••25
第六章.总结••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••26
致谢••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••27
参考文献•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••28
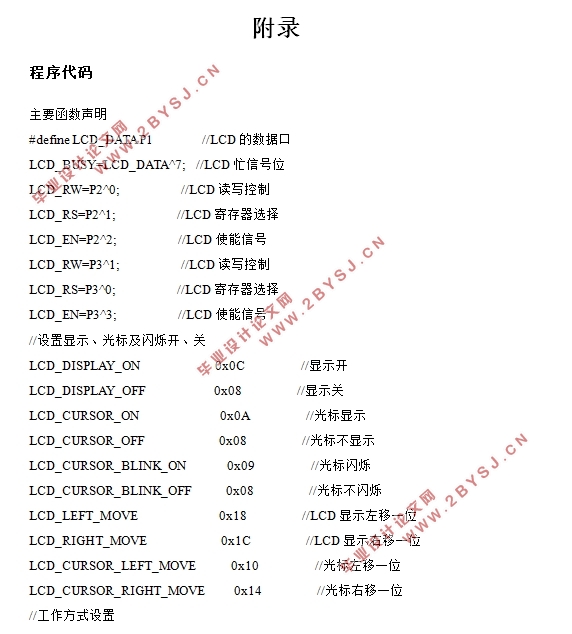
附录•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••30
