基于PLC的温室大棚智能温室控制系统设计
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
基于PLC的温室大棚智能温室控制系统设计(论文10000字)
摘 要
随着人们生活水平的提高,由温室大棚种植的反季节蔬菜成为人们越来越离不开的食物,农作物的生长环境能被温室大棚所改善,外界的四季变化和恶劣气候不会让其发生改变,创造了适宜农作物生长的环境。作为高效农业的重要部分——温室大棚,是我们值得研究的方向。
本论文主要介绍了温室大棚基于PLC控制的系统设计方案,为了对温室大棚中各项指标进行检测,该研究中将采用温度传感器、CO2浓度传感器、光照传感器,将测量值送入PLC中,在PLC中将其与设定值进行比较,再发出相应的指令驱动外围设备来调控温室大棚内的环境参数,从而实现了温室大棚的自动化、智能化控制。本设计的优点是成本低廉,节约资源,能实现利益最大化。
关键词:温室大棚;PLC;传感器;智能控制
ABSTRACT
With the improvement of people’s living standards, anti-season vegetables grown in greenhouses have become more and more indispensable for people. The growing environment of crops can be improved by greenhouses, and changes in the four seasons and bad weather will not allow them to occur. Change has created an environment suitable for the growth of crops. As an important part of high-efficiency agriculture, greenhouses are the directions that we should study.
This paper mainly introduces the system design scheme based on PLC control in greenhouses. In order to detect various indicators in greenhouses, this research will use temperature sensors, CO2 concentration sensors, light sensors, and send the measured values to the PLC. PLC will compare it with the set value, and then issue corresponding instructions to drive the peripheral equipment to regulate the environmental parameters in the greenhouse, thereby realizing the automation and intelligent control of the greenhouse. The advantages of this design are low cost, resource conservation, and maximized benefits.
Key words:Greenhouse;PLC;Temperature Sensor;Intelligent control
目 录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1课题背景 1
1.2研究目的和意义 1
1.3国内外研究现状 2
第二章 系统总设计方案 3
2.1系统的设计任务 3
2.2系统的控制方案 4
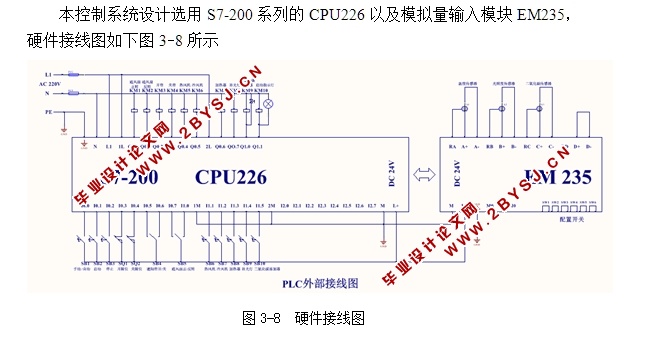
第三章 控制系统硬件方案设计 5
3.1电气控制系统主电路设计 5
3.2电气控制系统各部分控制电路设计 5
3.3PLC硬件电路设计 9
3.4传感器型号选择 11
第四章 控制系统软件方案设计 14
4.1STEP7 Micro/Win软件简介 14
4.2控制系统程序设计思路 14
4.3控制系统程序流程图 15
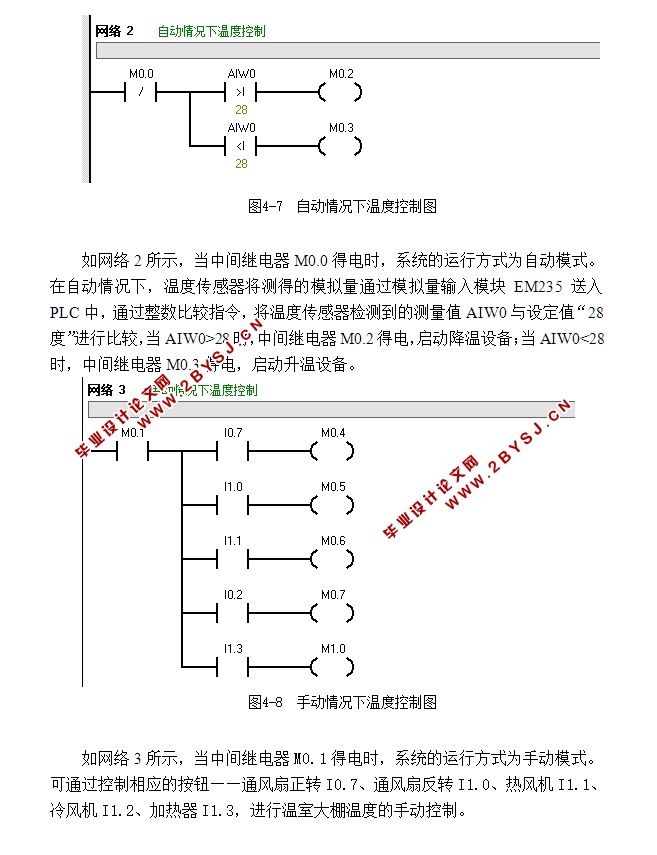
4.4控制程序设计及分析 16
第五章 控制程序的仿真与调试 24
5.1仿真软件介绍 24
5.2仿真与调试准备工作 24
5.3程序仿真与调试 24
结论 26
致谢 27
参考文献 28
