基于单片机的简易计算器设计
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
基于单片机的简易计算器设计(任务书,开题报告,论文9000字)
摘要
在信息和技术飞速发展的今天,单片机技术也在不断地进步,单片机在生活中的应用也是日益广泛。计算器在生活中的很多地方都不可或缺,但是究竟如何才能让计算器技术变得更加成熟,也依旧是当前研究的重要课题。与此同时,单片机由于其性能优越,在很多行业得到了广泛使用,如电子信息、科技、交通、通信等领域。它价格便宜,所以用单片机来设计一款简易电子计算器很有研究意义,也具有很强的推广性。
本次设计以51单片机为核心,采用4*4的矩阵键盘作为输入按键,最终能够进行数字的加法、减法、乘法和除法运算,并最多支持12位数字的运算,通过调试和仿真之后能够在1602液晶屏上显示输入过程和运算结果,显示结果时会显示六位数,当结果多余六位数时会以科学计数法的形式显示。
关键词:计算器 AT89C52 Proteus C语言 模拟仿真
Design of simple Calculator based on single Chip Microcomputer
Abstract
With the rapid development of information and technology, single-chip microcomputer technology is also constantly improving, and the application of single-chip microcomputer in life is becoming more and more extensive. Calculator is indispensable in many parts of life, but how to make calculator technology become more mature is still an important research topic.At the same time, because of its superior performance, single-chip microcomputer has been widely used in many industries, such as electronic information, science and technology, transportation, communications and other fields. It is cheap, so using single-chip microcomputer to design a simple electronic calculator is of great significance, but also has a strong promotion.
In this design, 51 single chip microcomputer is used as the core, and the matrix keyboard of 4*4 is used as the input keystrode. finally, the addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of numbers can be carried out, and up to 12 digits can be supported. After debugging and simulation, the input process and operation results can be displayed on the 1602 LCD screen, and the six digits will be displayed when the results are displayed, and the results will be displayed in the form of scientific counting method when the results are redundant.
Key words:calculator; AT89C52; Proteus; C language; simulation
目录
摘要 i
Abstract ii
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 系统开发的背景 1
1.2 系统开发的意义 1
1.3 设计目的 1
1.4 实现方案 1
第二章 系统总体方案和设计 2
2.1设计思路分析 2
2.2 系统总体组成及框架图 2
2.3 元器件选择以及软件介绍 3
2.3.1 主要使用的元器件 3
2.3.2 系统主要使用软件 4
2.3.3 编程电路设计平台 4
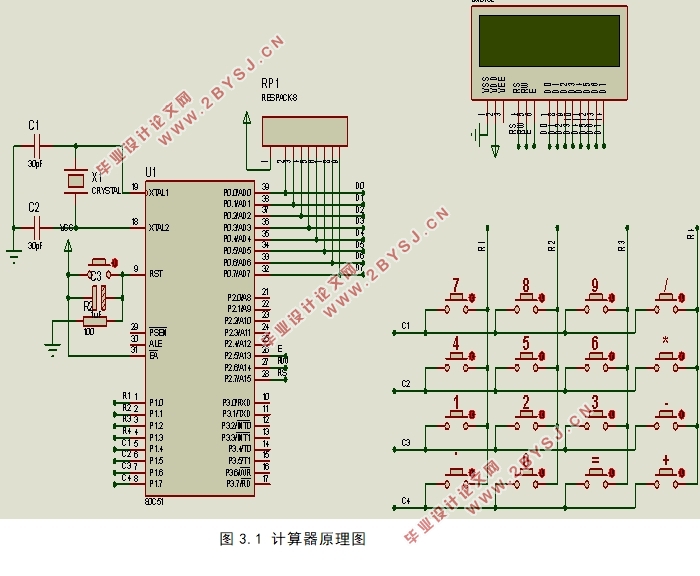
第三章 硬件电路设计 6
3.1 设计方案的确定 6
3.2 系统硬件设计 6
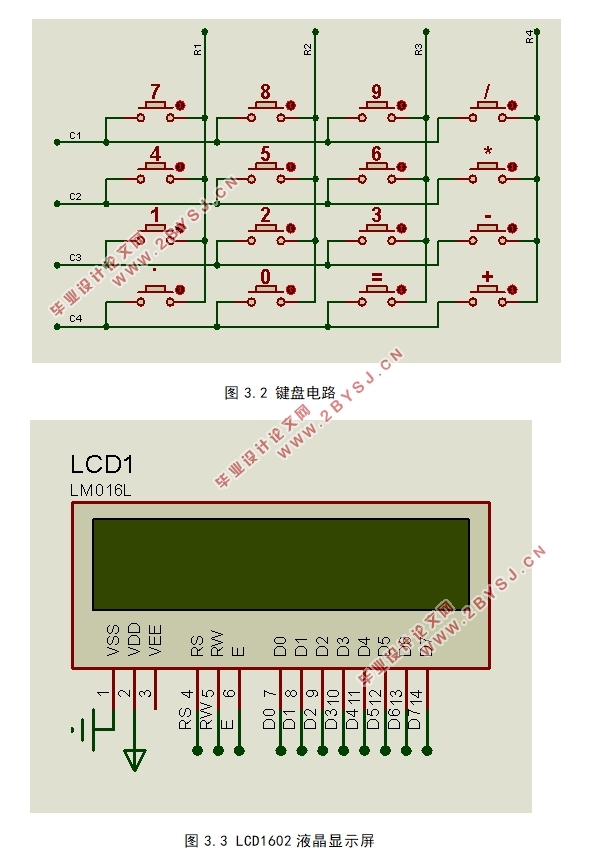
3.2.1 键盘电路模块 7
3.2.2 显示电路模块 7
第四章 软件设计 9
4.1主程序的设计 9
4.2 子程序模块 9
4.2.1 键盘扫描的程序设计 9
4.2.2显示模块的程序设计 15
第五章 系统的仿真与调试 17
5.1 调试步骤 17
5.2 仿真及结果验证 17
5.2.1 检测正常启动及屏幕发光 17
5.2.2 检测计算功能 18
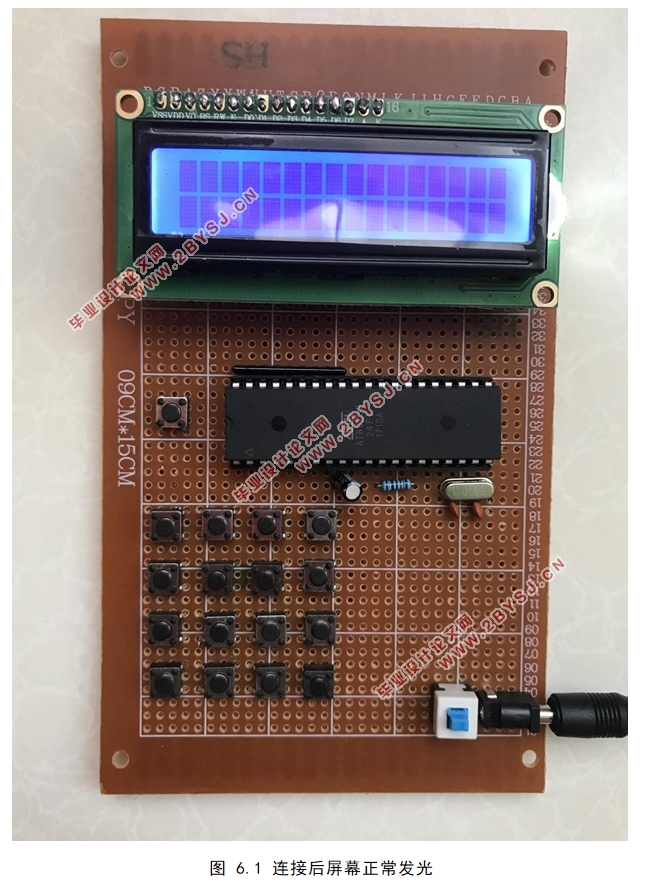
第六章 实物的制作与测试 24
6.1 实物制作过程 24
6.2计算器的正常启动以及功能测试 24
6.2.1 检测计算器是否可以正常启动 24
6.2.2 检测计算功能 25
第七章 总结与展望 33
参考文献 34
致谢 36
