200T门座起重机总体及人字架结构设计(含CAD,SolidWorks三维图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
200T门座起重机总体及人字架结构设计(含CAD,SolidWorks三维图)(任务书,开题报告,论文说明书16000字,CAD图5张,SolidWorks三维图)
摘 要
当前,造船用门座起重机相对于港口用门座起重机与电站建筑用门座起重机来说有较快发展,其最主要特点是起重量大、吊装准确可靠和工作运行速度慢。人字架作为门座起重机的主要构件之一,与转台、转柱构成了门座起重机臂架系统和平衡系统的支承结构,承载了吊重、臂架系统、以及配重和变幅平台。它的安全稳定直接关系到门座起重机的安全,对人字架结构的力学分析具有重要意义。
本文选取200T造船用门座起重机为研究对象,完成总体设计计算和人字架结构设计计算。同时,利用SolidWorks三维建模软件和ANSYS Workbench大型有限元分析程序完成对人字架的模型创建与结构静力分析,得到人字架在不同工作幅度和不同受载情况下的变形等值线云图和应力等值线云图,为人字架结构优化设计提供理论依据。
关键词: 门座起重机,人字架,静力学分析,有限元,优化设计
Abstract
At present, shipyard portal crane compared to the port with the harbour portal crane and power station crane bears more advantages thatit develops faster, carries more weight with an accurate and reliable lifting.Besides, slow operation is its most important features. The herringbone frame is one of the main components of the portal crane, which forms the supporting structure of the portal crane system and the balance system with the turntable and the column, which carries the hoisting, the boom system, the counterweight and the landing platform. Its safety and stability is directly related to the safety of portal crane, which poses a grave importance to the mechanical analysis of herringbone frame structure.
200T shipyard portal crane is regarded as the object of the design, with complete the overall calculation of design and the design of humanoid frame. At the same time, I use the SolidWorks 3D modeling software and the ANSYS Workbench large-scale finite element analysis program to complete the modeling and structural static analysis of the herringbone frame, obtaining contours of the herringbone frame under different working ranges and different load conditions.,which provides the theoretical design basis for the optimization design of the herringbone frame structure.
Key words: Portal cranes , Herringbone frame , Static analysis , Finite element ,
Finite element
设计要求
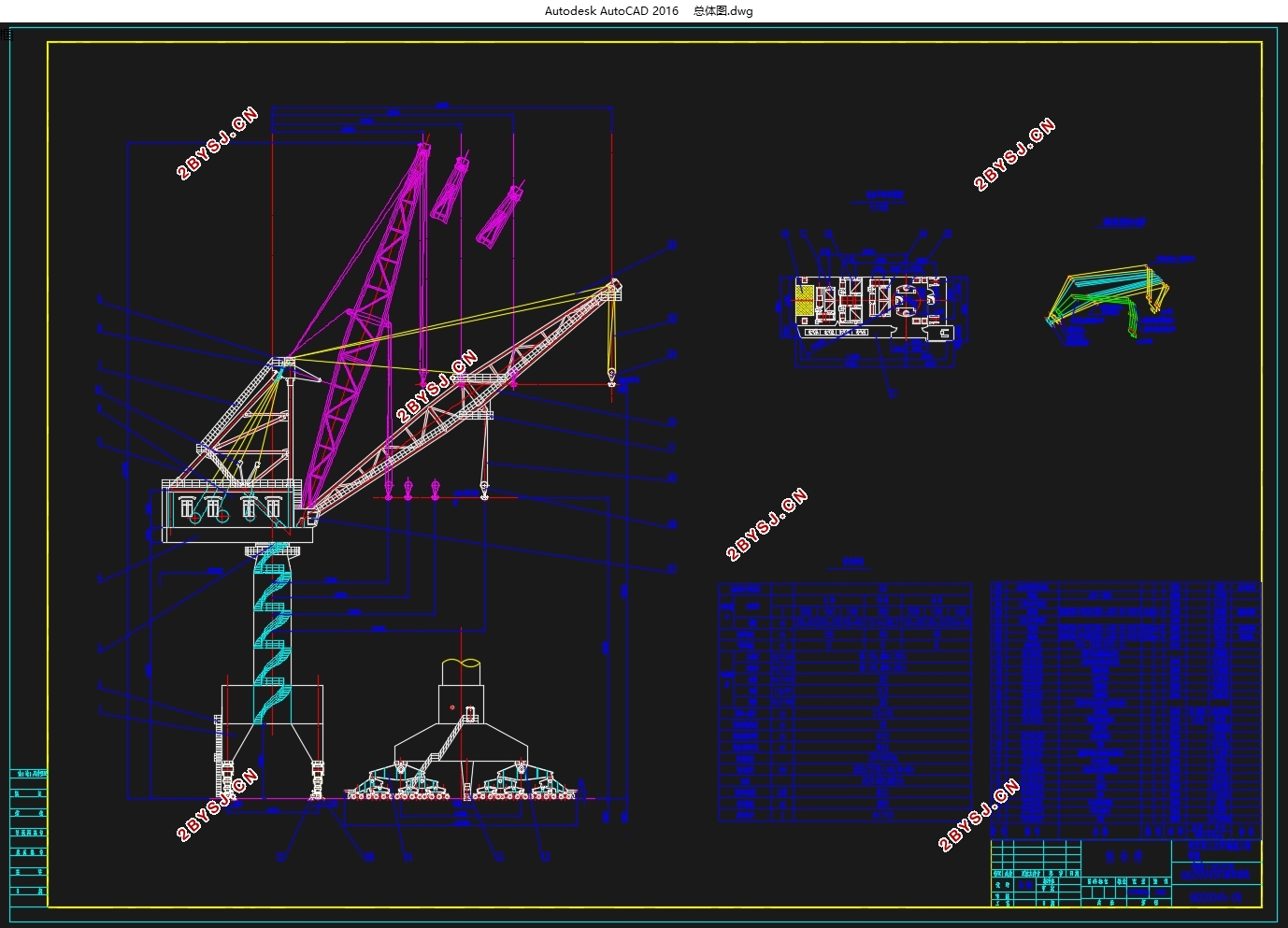
本机用于某造船厂船体安装用门座起重机,以吊钩作为取物装置,具有较大起重量、工作速度较缓慢和吊装可靠准确的工作特点。在满足船厂造、修大型船舶的工作需求的同时,应当合理设计起重机结构外形,尽量使外形尺寸小且有较高门架[1]。
基本参数
基本参数是起重机作业性能指标的表征,也是起重机设计的基本依据[5]。包括:起重量、起升高度(下降深度)、工作速度、轨距、轮压、工作级别等,本机基本参数具体见表2.1。
表2.1 基本参数表
工作级别 整机 起升机构 回转机构 变幅机构 运行机构
A4 M5 M4 M4 M5
起重能力 起重量 主钩 副钩 抬吊
t 200 150 100 100 200 150 100
幅度 m 20~25 20~32 20~45 15.4~28.1 20~25 20~32 20~45
起升高度 m 55 40 40
下降深度 m 5 5 5
机构速度 主起升 m/min 8(16,载荷<70t)
副起升 m/min 8(16,载荷<35t)
变幅 m/min 20
旋转 r/min 0.3
行走 m/min 30
轨距×基距 m 12×16
门架净空高度 m 10
转盘尾部半径 m 约15
转盘尾部净高 m 约34
轨道型号 CR100Kg
最大轮压 kN 390/270(工作/静止)
电源 AC440V,60Hz







目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 门座起重机简述 1
1.2 门座起重机分类 1
1.3 门座起重机国内外发展现状 1
1.3.1 国内发展现状 1
1.3.2 国外发展现状 2
1.4 门座起重机发展趋势 3
1.4.1 借助计算机的现代化设计 3
1.4.2 依托中国创造的中国制造 3
1.4.3智能化控制的系统化发展 3
1.5 选题意义 4
第2章 总体设计 5
2.1 设计要求 5
2.2 基本参数 5
2.3 载荷计算 5
2.3.1 自重载荷(PG) 5
2.3.2 起升载荷(PQ) 6
2.3.3 运行冲击载荷 7
2.3.4 惯性载荷 8
2.3.4.1 运行水平惯性力(PH) 8
2.3.4.2 回转运动水平惯性力 9
2.3.4.3 偏摆角α 10
2.3.5 偏斜运行时水平侧向载荷PS 10
2.3.5.1 ∑P计算 10
2.3.5.2 侧向载荷系数λ确定 11
2.3.6 风载荷PW 12
2.3.6.1 计算风压p 12
2.3.6.2 风压高度变化系数Kh 13
2.3.6.3 有效迎风面积A 13
2.3.6.4 风力系数C 13
2.4 轮压计算 15
2.4.1 支承反力计算 16
2.4.2 轮压计算 17
2.5 抗倾覆稳定性计算 19
2.5.1 起重机类别、工况和计算载荷确定 19
2.5.2 臂架位置和倾覆线确定 19
2.5.3 抗倾覆稳定性计算校核 20
2.5.3.1 无风试验或运行 20
2.5.3.2 有风工作或运行 21
2.5.3.3 突然卸载或吊具脱落 23
2.5.3.4 暴风侵袭 24
第3章 金属结构设计 25
3.1 设计方法概述 25
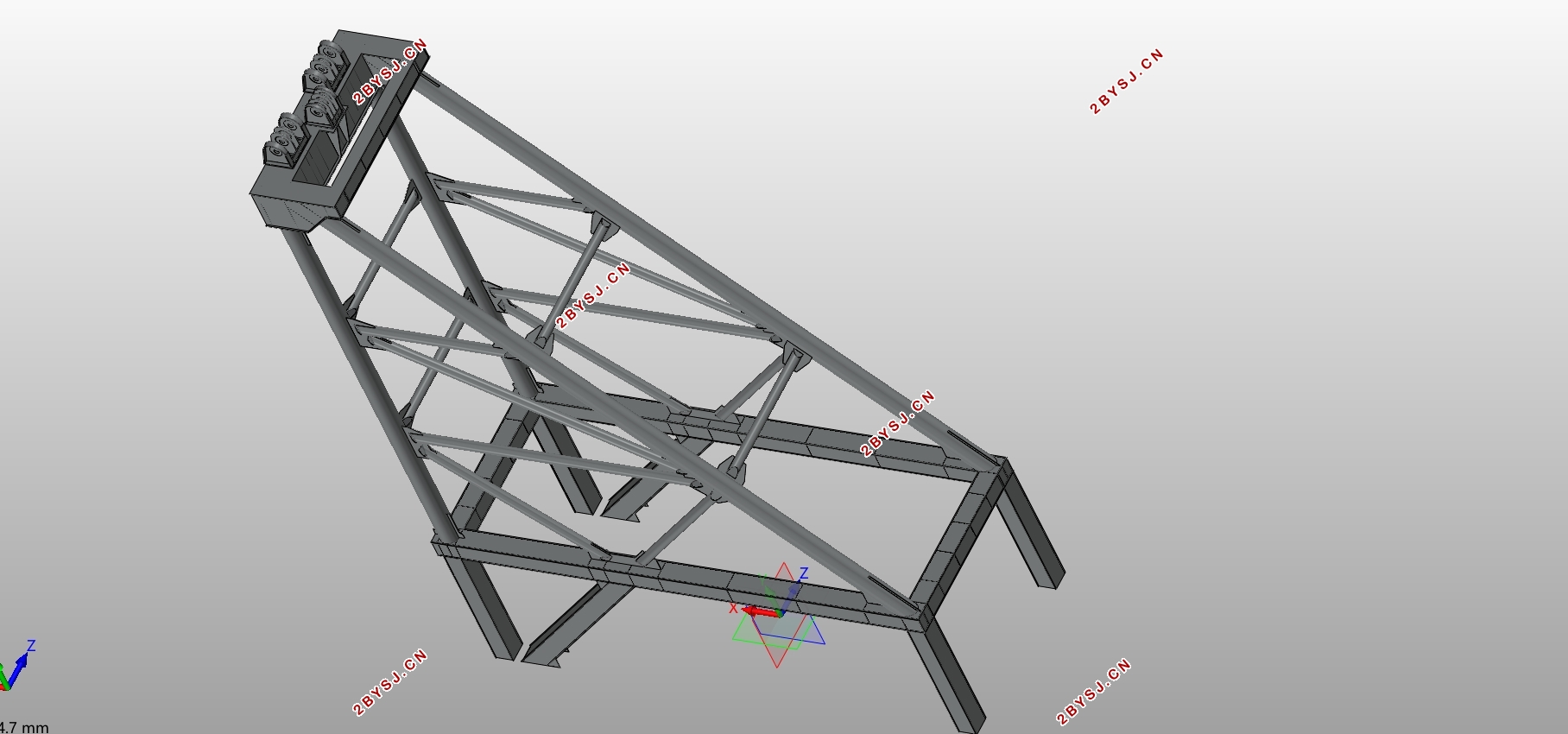
3.2 人字架结构设计 25
3.2.1 计算简图 25
3.2.2 载荷计算 25
3.2.3 载荷计算方法 26
3.3人字架结构有限元分析 27
3.3.1 有限元计算简图 27
3.3.2 结构材料选择及模型建立 27
3.3.2.1 结构材料选择 27
3.3.2.2 模型建立 27
3.3.3 有限元分析 28
第4章 经济性与环境影响分析 32
4.1经济性分析 32
4.1.1 自重轻型化 32
4.1.2 材料的选择 32
4.1.3 零件的选择 32
4.2 环境影响分析 33
第5章 总结与展望 34
5.1 总结 34
5.2 不足与展望 34
5.2.1 不足 34
5.2.2 展望 34
参考文献 36
附录A 37
致谢 38
