仿人柔性机械手构型设计及运动学仿真分析(含CAD图,CATIA三维图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
仿人柔性机械手构型设计及运动学仿真分析(含CAD图,CATIA三维图)(任务书,开题报告,文献摘要,论文说明书34000字,CAD图纸4张,CATIA三维图)
摘 要
本文完成了仿人机械手调研-构型选型设计-运动学仿真的整个过程,所设计的机械手具有结构简单、驱动和传动方便等优点。具体而言,本文在调研大量国内外仿人机械手的运动学结构和自由度的基础上,依据仿生学和人手解剖学的原理,首先完成了对仿人柔性机械手的结构选型和构型设计。其次,运用D-H参数法建立了单个手指的运动学模型,并在机器人工具箱中对其正确性进行了验证。在虚拟样机中对整个机械手进行了运动学仿真分析。研究发现:在所给驱动条件下机械手能很好地完成运动学仿真,且各个关节的角位移和角速度曲线亦证明本文所设计的机械手结构的合理性。另外,以机械手拇指和食指为例,用其雅可比矩阵转置阵 条件数倒数 的分布情况作为指标,证明手指机构具有较好的各向同性操作性能,其运动学参数的设计是合理的。在虚拟样机软件ADAMS中对机械手的抓持性能进行仿真,结果表明本文设计的机械手符合设计要求,满足机械手在生活服务中的基本功能需求。
本文完成了仿人机械手从调研到构型选型设计到运动学仿真的整个过程。设计的机械手具有结构简单、驱动和传动方便等优点,进一步优化外形和添加数字控制系统后,有望在日常生活中进行推广应用。
关键词:仿人机械手;D-H参数;运动学仿真;抓持仿真
Abstract
This paper has completed the entire process of humanoid robot research-construction selection design-kinematics simulation. The designed robot has the advantages of simple structure, convenient drive and transmission. Specifically, based on the study of a large number of kinematic structures and degrees of freedom of human-like manipulators at home and abroad, this paper first completed the structural selection and configuration design of humanoid flexible manipulators based on the principles of bionics and human hand anatomy. . Second, the kinematics model of a single finger was established using the D-H parameter method, and its correctness was verified in the robot toolbox. The kinematic simulation analysis was performed on the entire manipulator in the virtual prototype. The study found that the kinematics simulation can be well performed by the manipulator under the given driving conditions, and the angular displacement and angular velocity curves of each joint also prove the rationality of the manipulator structure designed in this paper. In addition, taking the thumb and index finger of the robot as an example, the distribution of the reciprocal of the matrix condition of the Jacobian matrix is used as an indicator to prove that the finger mechanism has good isotropic operation performance and the kinematics parameters are designed rationally. In the virtual prototype software ADAMS, the gripping performance of the manipulator is simulated. The results show that the manipulator designed in this paper meets the design requirements and meets the basic functional requirements of manipulators in life services.This paper completes the entire process of humanoid manipulators from investigation to configuration selection design to kinematics simulation. The designed manipulator has the advantages of simple structure, convenient driving and transmission, etc. After further optimizing the appearance and adding the control system, it is expected to be popularized and applied in daily life.
This paper completes the entire process of humanoid manipulators from investigation to configuration selection design to kinematics simulation. The designed manipulator has the advantages of simple structure, convenient driving and transmission, etc. After further optimizing the appearance and adding a digital control system, it is expected to be popularized and applied in daily life.
Keywords: humanoid manipulator; D-H parameter; kinematics simulation; gripping simulation
总体方案布局与设计原则
仿人机械手的设计指标和功能参数是依据其用途来确定的。本文设计的机械手目的是快速地运用到人类生活的各个方面,例如用作医疗机械手。保障和提高残疾人、老年人等弱势群体的生活质量。仿人机械手的设计要考虑机械手的构型、自由度、传感器的型号类别以及体积和驱动器的型号功率等因素[29]。
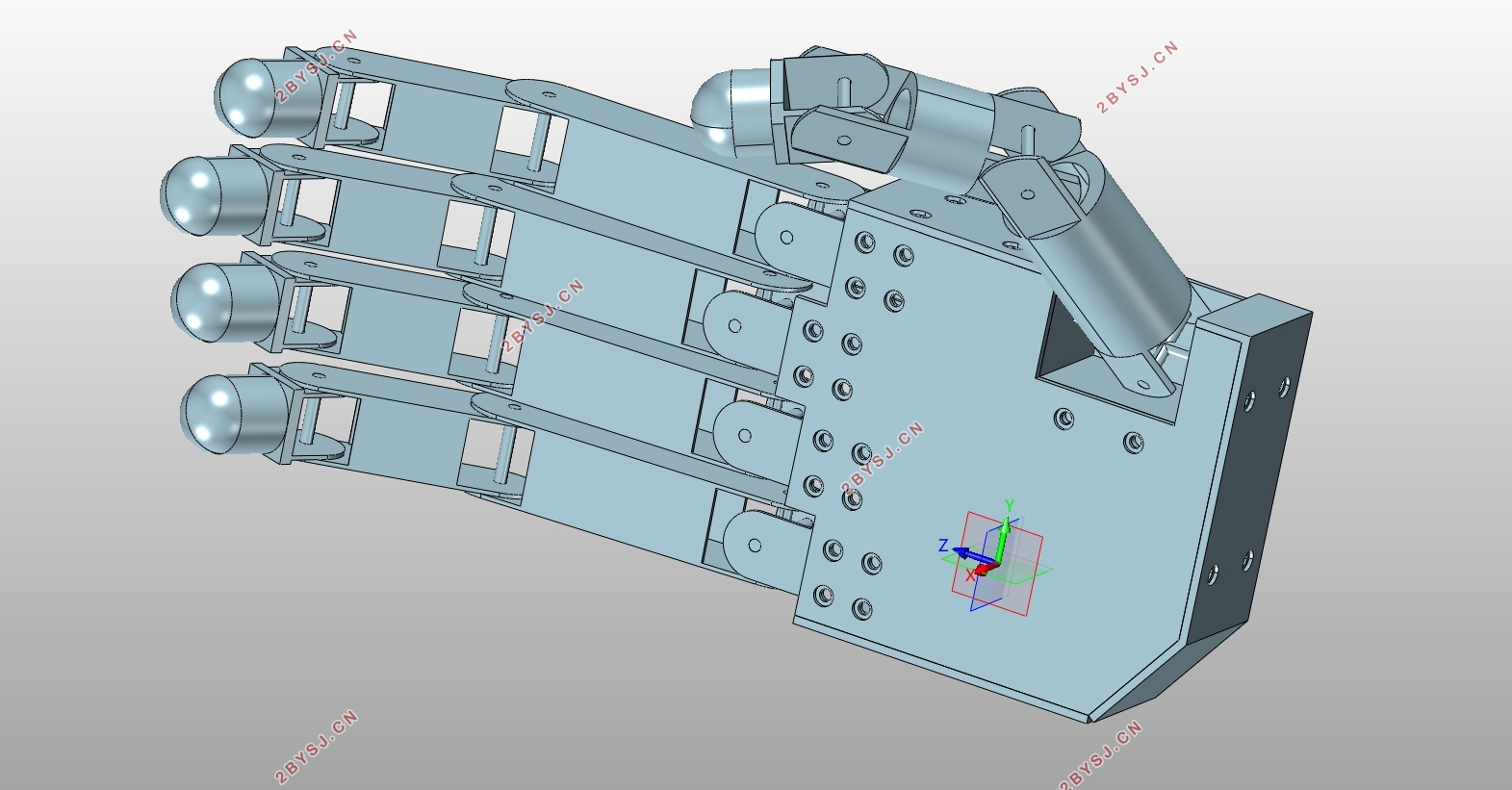
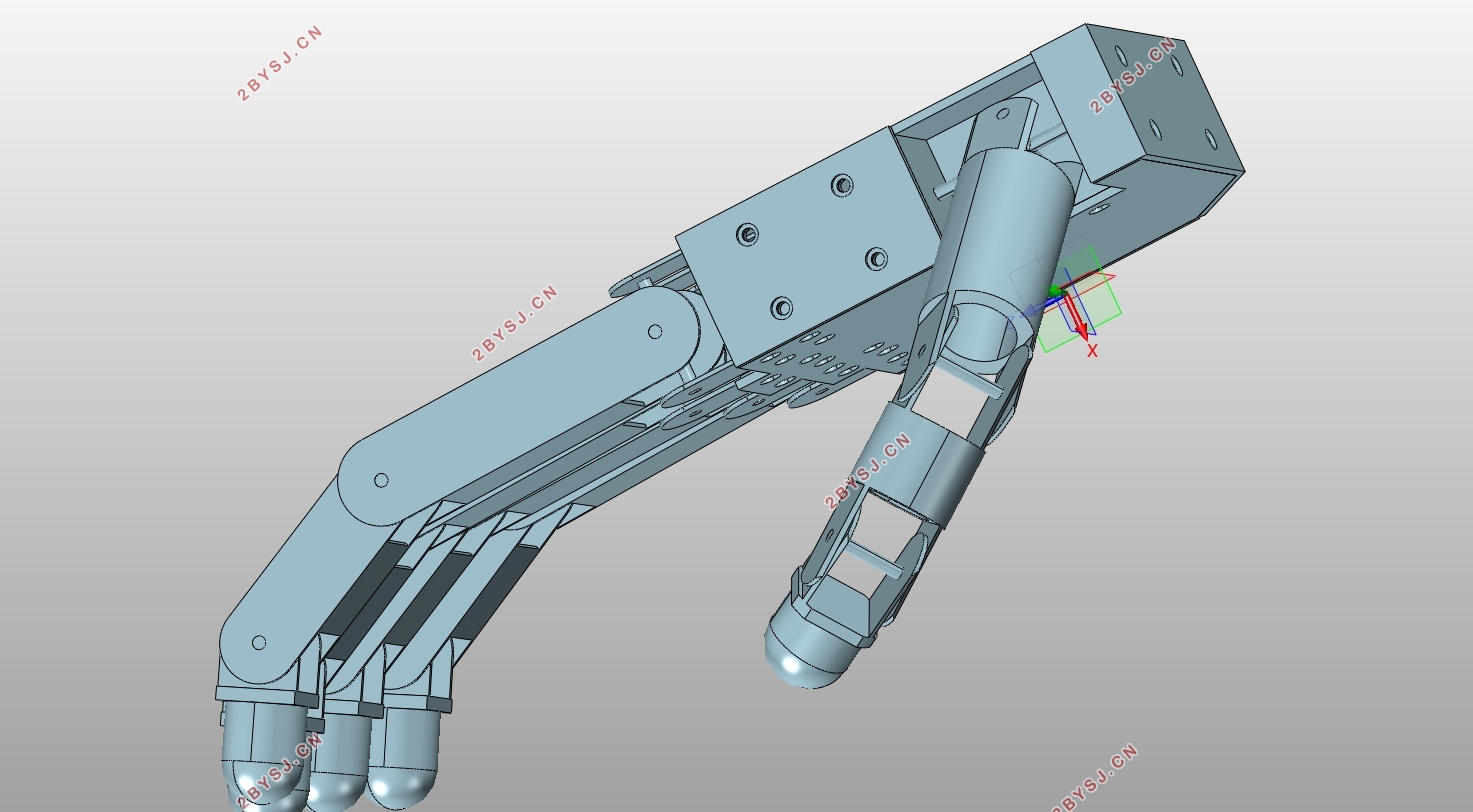
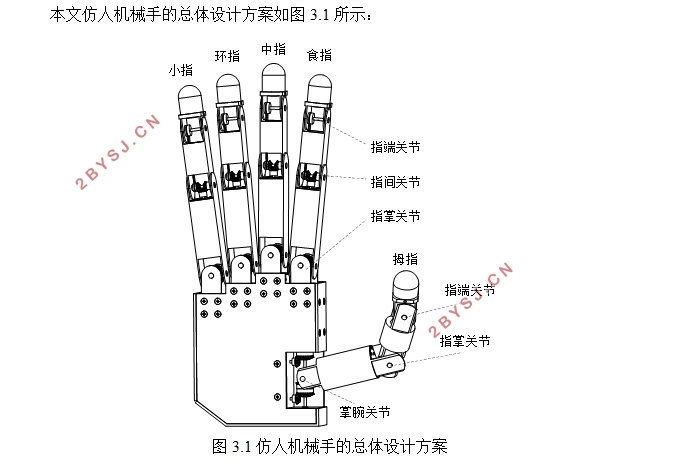
本文仿人机械手的总体设计方案如图3.1所示:
图3.1仿人机械手的总体设计方案
机械手自由度的选取仿照人手的自由度,在满足机械手基本功能的前期下,尽量减少自由度的数目。这样可以节约成本,减小机械手的体积和驱动器的数量,有利于减轻重量实现模块化设计。也更有利于机械手使用范围的扩大。这样做还有两个更加深层次的原因:
(1)协调传感器和控制器所能达到的水平。虽然我们要具有更好的灵巧性,但如果传感和控制的难度比较大,反而无法充分发挥机械手多自由度的优势。
(2)机械手功能的强弱与其自由度之间的关系还没有一个确定的数学描述。盲目的追求自由度、灵活性反而增加设计难度,需求和功能脱节。
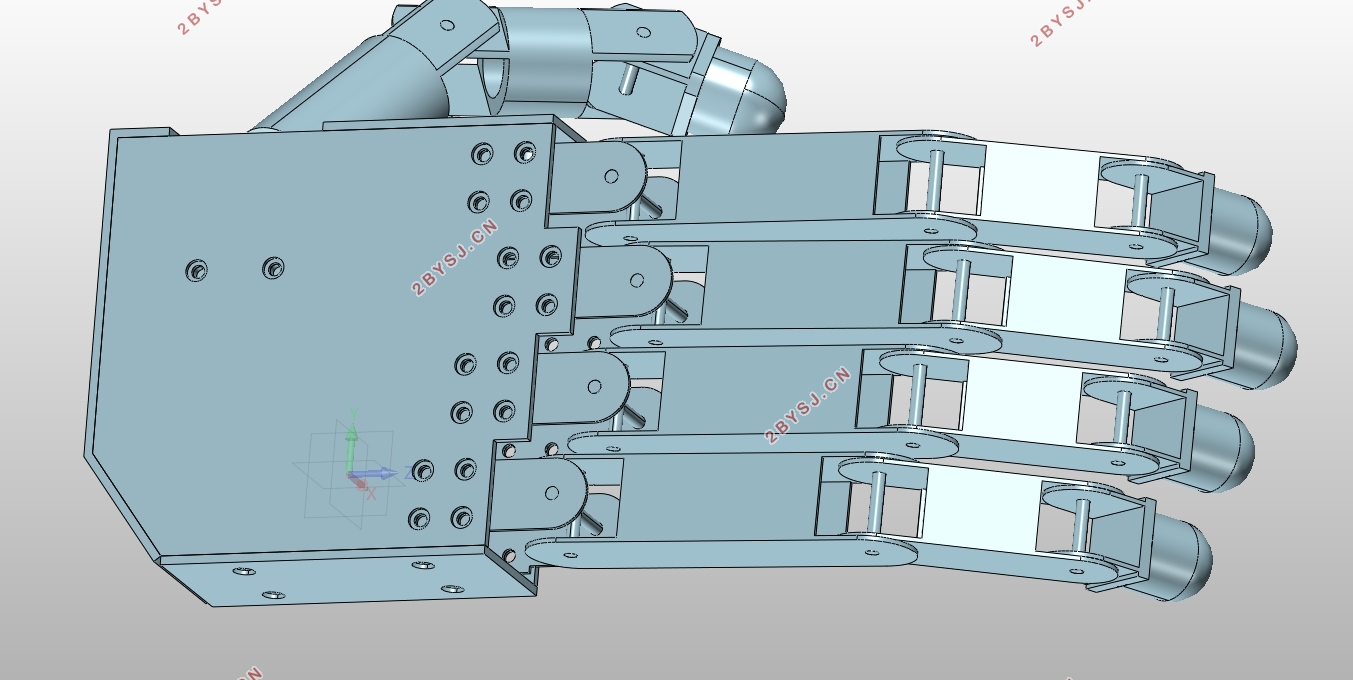
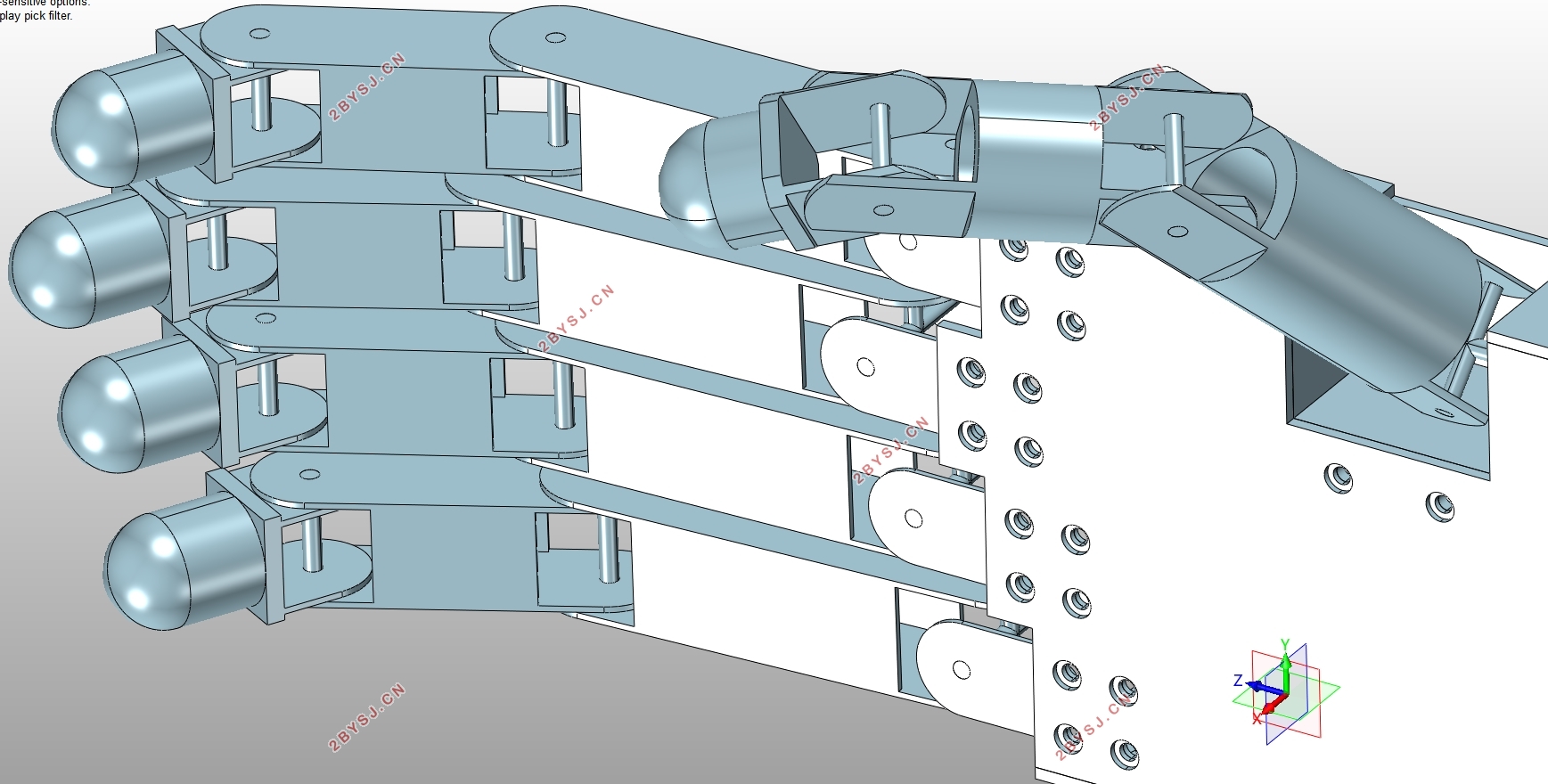
指关节和指节的命名与人类手掌相同。其整手的自由度分配方式如下:拇指有三个自由度,其中掌腕关节有两个自由度,指掌关节有一个自由度。其余4指完全相同,各三个自由度。其中指掌关节两个自由度,指间关节一个自由度。这些关节都为由电动机驱动的主动关节,其他各关节为与主动关节耦合运动的被动关节。在各手指的指端安装有六维力、力矩传感器,主动各关节上安装有角位移传感器。依据对机械手的调研和其在生活中的应用情景,设定的其他技术指标如下所示:
(1)指端法向力不小于10N;
(2)整个手掌的重量不大于1.5kg;
(3)构型尺寸尽量接近人类手掌;
(4)手指各主动关节速度大于1rad/s;
(5)手指各关节的运动范围参考人类手掌。
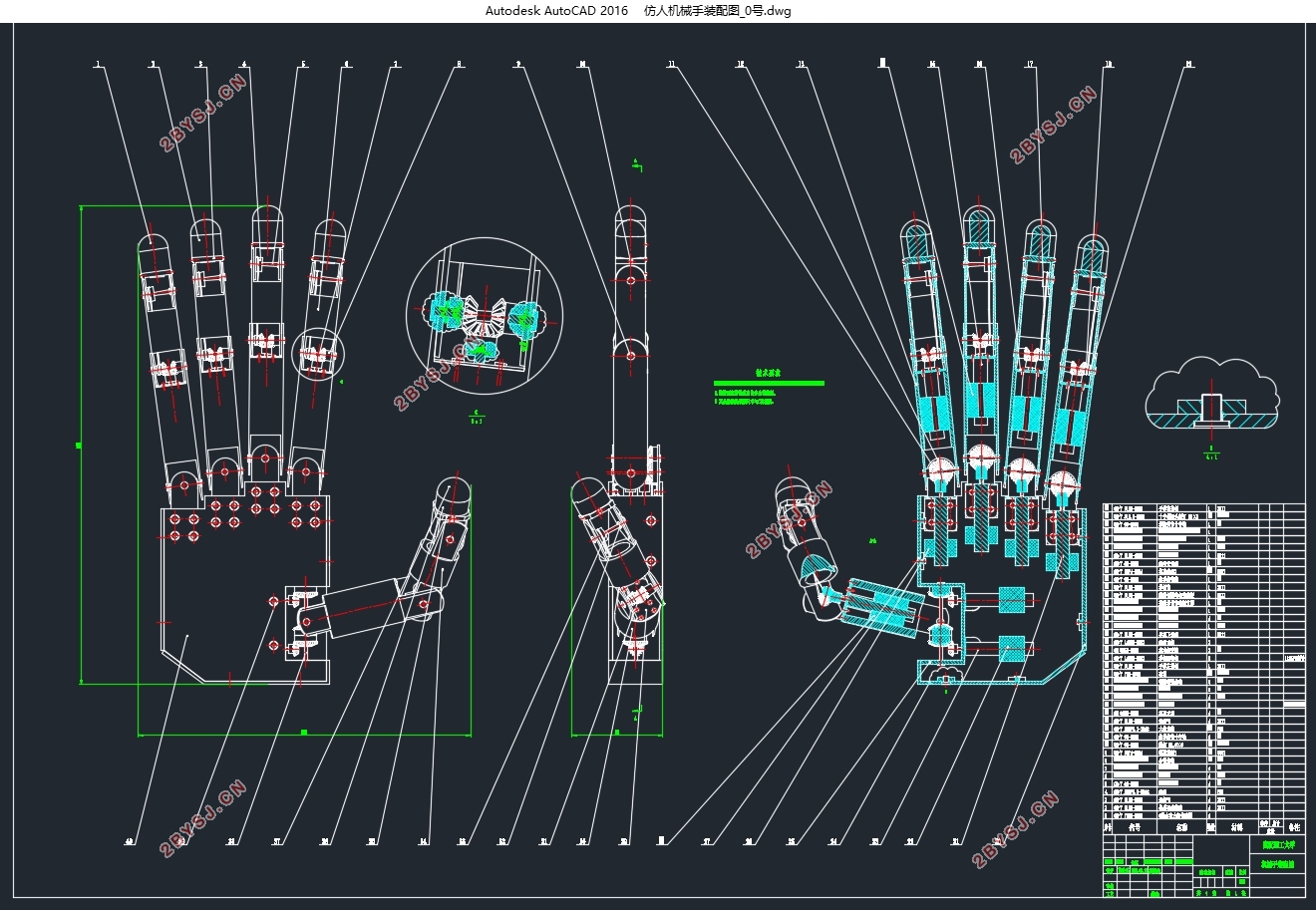
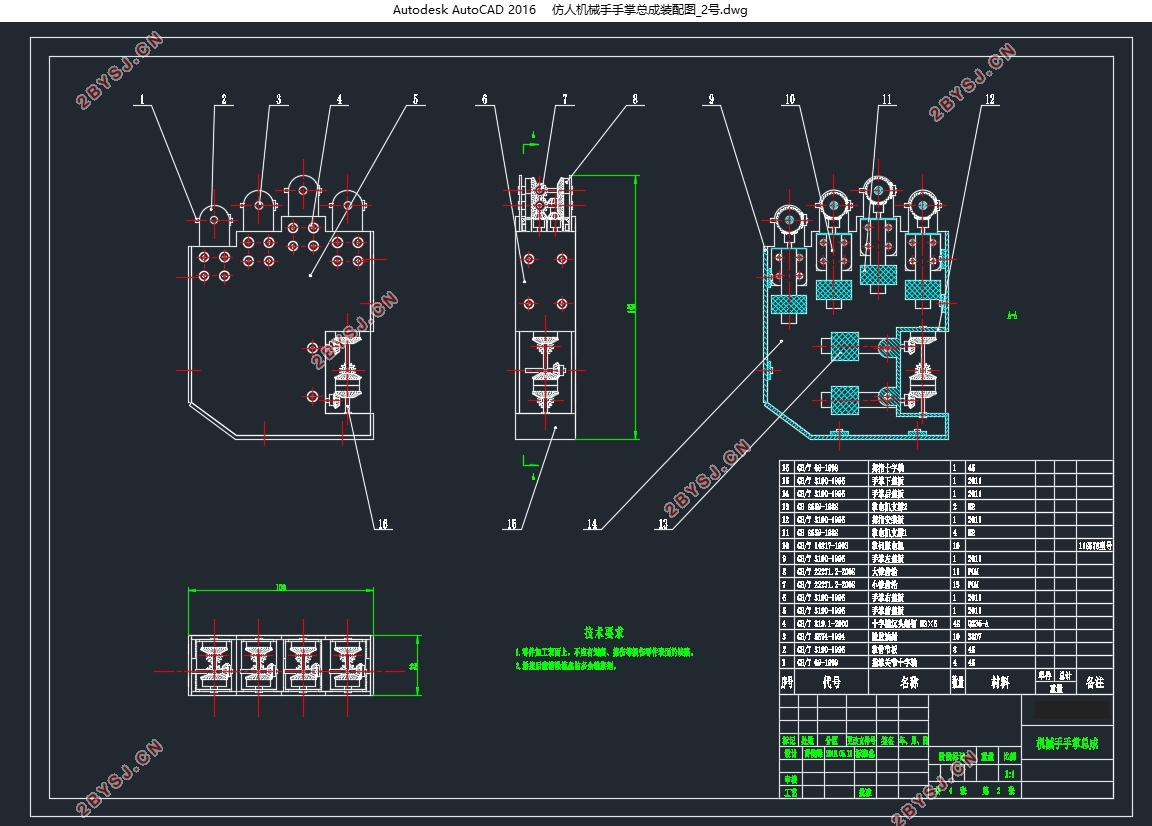
机械手是由手掌和手指连接而成,其功能的强弱与手指机械结构设计和驱动传动布置有关,也与五个手指在手掌上的相对位置有密切关系[30]。本文机械手的设计样例,是直接模仿人手的构型。拇指掌腕关节安装于手掌的侧下方,在手掌上的相对尺寸位置与人类手掌成一定比例设计。拇指十字轴的安装方式与其他四指有区别,拇指是屈曲轴与手掌安装在一起,而其余四指是侧摆轴与手掌安装为一体[18]。
机械手构型的设计,主要有四个方面的内容:
(1)手指机构构型设计;
(2)手指的驱动设计;
(3)手指的传动设计;
(4)拇指和手掌的结构设计。


目录
第1章绪论 1
1.1 研究背景及意义 1
1.2 仿人机械手的研究概况 1
1.2.1 外置型仿人机械手的研究综述 2
1.2.2 内置型仿人机械手的研究综述 5
1.3 仿人机械手的关键技术 10
1.3.1 轻巧强大的驱动 10
1.3.2 灵敏多样的传感器 10
1.3.3 快速智能的控制 10
1.4 本文的主要研究内容 11
第2章仿人机械手结构选型 12
2.1 引言 12
2.2 仿生学及人手解剖学简介 12
2.2.1 仿生学介绍 12
2.2.2 人手解剖学介绍 13
2.3 仿人机械手灵巧性简介 16
2.3.1 灵巧性介绍 16
2.3.2 最小指数与最小关节 17
2.4 仿人机械手结构选型 19
2.4.1 手指运动副的形式 19
2.4.2 手指数量的确定 20
2.4.3 手掌的结构 22
2.4.4 手指的截面结构形式 23
2.4.5 手指的材料 24
2.4.6 手指的驱动方式 24
2.4.7 手指的传动方式 26
2.5 机械手结构选型总结 27
2.6 本章小结 28
第3章仿人机械手构型设计 29
3.1 总体方案布局与设计原则 29
3.2 手指机构构型设计 30
3.3 手指的驱动设计 32
3.4 手指的传动结构设计 32
3.4.1 四指传动结构设计 33
3.4.2 拇指和手掌的结构设计 37
3.5 机械手设计指标的校核 39
3.6 本章小结 41
第4章仿人机械手运动学分析与仿真 42
4.1 机械手运动学分析介绍 42
4.2 手指机构运动学分析 42
4.2.1 手指机构坐标系的建立 42
4.2.2 手指机构正运动学分析 44
4.2.3 手指机构逆运动学分析 47
4.3 手指运动学验证与仿真 50
4.3.1 构建手指对象 51
4.3.2 模型验证 52
4.3.3 手指正运动学仿真 52
4.3.4 手指逆运动学仿真 53
4.3.5 轨迹规划 54
4.4 仿人机械手的运动学仿真 55
4.4.1 三维模型的建立导入和参数设定 55
4.4.2 虚拟样机驱动的设定 56
4.4.3 仿真结果分析 57
4.4.4 运动学方程验证 60
4.5 本章小结 60
第5章仿人机械手操作性能分析和抓持仿真 61
5.1 仿人机械手操作性能分析 61
5.2 仿人机械手抓持仿真 64
5.3 本章小结 65
第6章总结与展望 66
6.1 本文总结 66
6.2 仿人机械手未来展望 66
参考文献 68
附录 71
致谢 76
