新能源汽车盘式制动器设计(英文版)(含CAD图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
新能源汽车盘式制动器设计(英文版)(含CAD图)(任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,文献摘要,论文说明书英文版14000字,CAD图3张)
Summary
The automobile brake system plays an important role in ensuring the safety of the vehicle, the reliability of the parking and the economic benefits of transportation. With the rapid development of the expressway, the increase of the speed and the increasing traffic density, the brake system of the automobile Work reliability is becoming increasingly important, so many brake regulations place many detailed and specific requirements on the brake system. The stable braking performance of the disc brakes has gradually replaced the drum brakes. Therefore, it is important to design a disc brake that is stable and safe and reliable. With the increase in the level of highways, the rise in the number of passengers, especially the enforcement of national safety regulations, the use of disc brakes in the front and rear wheels will be a trend. In this design, reference is made to the design concepts of some foreign advanced disc brakes. Through the analysis of the main parameters of the brake system, it is determined as the floating caliper disc brake, and the structural analysis and design calculation are carried out, and the assembly drawing of the front wheel brake and the parts drawing of the brake disc are drawn, and the relevant evaluation indexes are also complete. meets the. The final design of the brakes basically achieved the desired goal.
Keywords: disc brake; parameter design;performance;check

Contents
ChapterⅠIntroduction 1
1.1 The meaning of brake design 1
1.2 Brake development history 1
1.3 Application of domestic disc brakes 2
1.4 Application of foreign disc brakes 5
1.5 Current development status of brakes 7
Chapter II Structure and Design Principles of Brakes 17
2.1 Automotive brake system function and classification 17
2.2 Classification and introduction of disc brakes 17
2.3 Disc brake structure and working principle 20
2.4 General principles of brake design 21
2.4.1 Brake performance 21
2.4.2 Brake performance stability 22
2.4.3 Brake clearance adjustment simplicity 22
2.4.4 Brake size and quality 23
2.4.5 Noise reduction 23
Chapter III Brake Design 24
3.1Design Parameters 24
The original parameters of this design refer to the design specification. 24
3.2 Main components of disc brakes 24
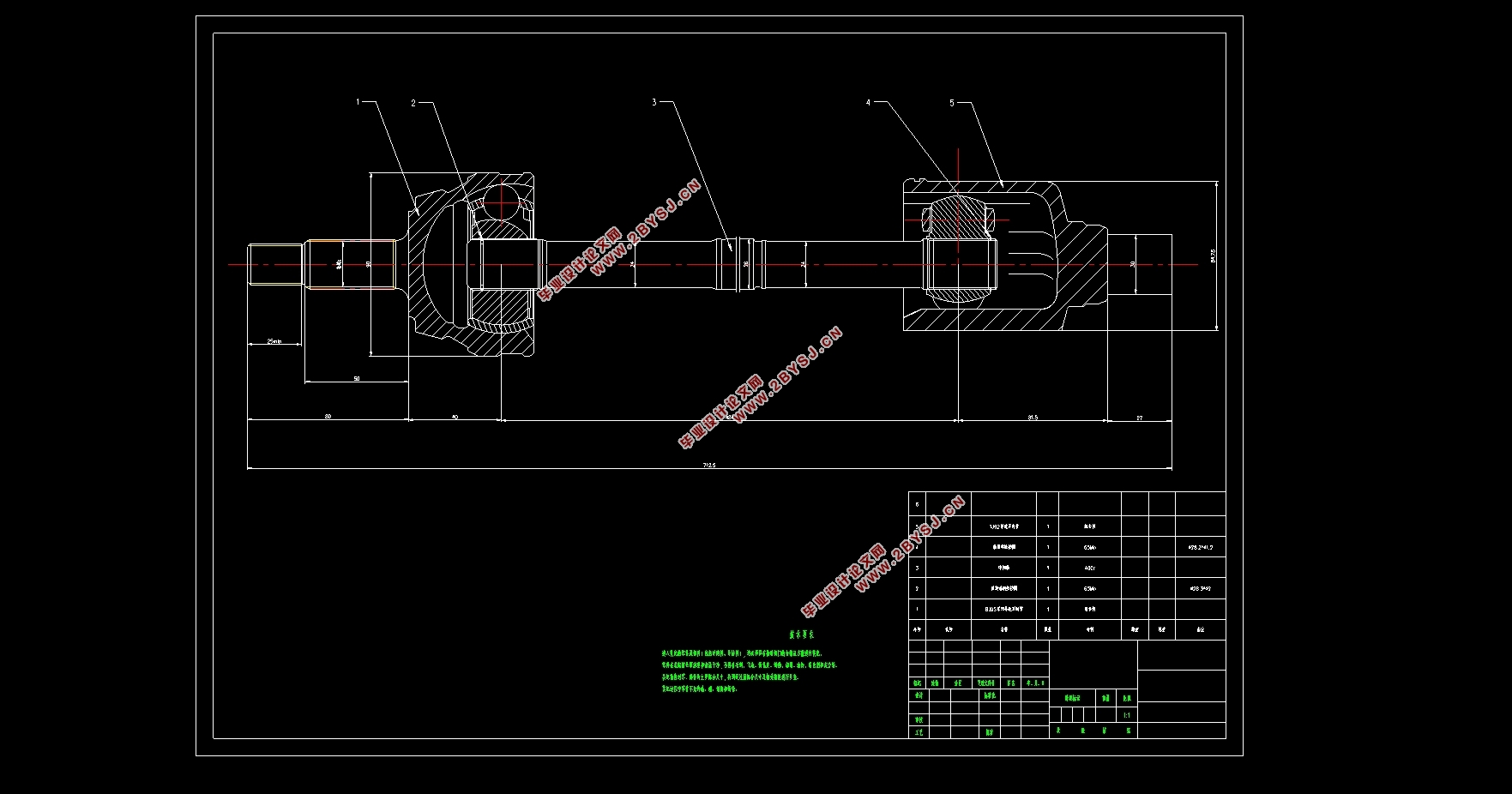
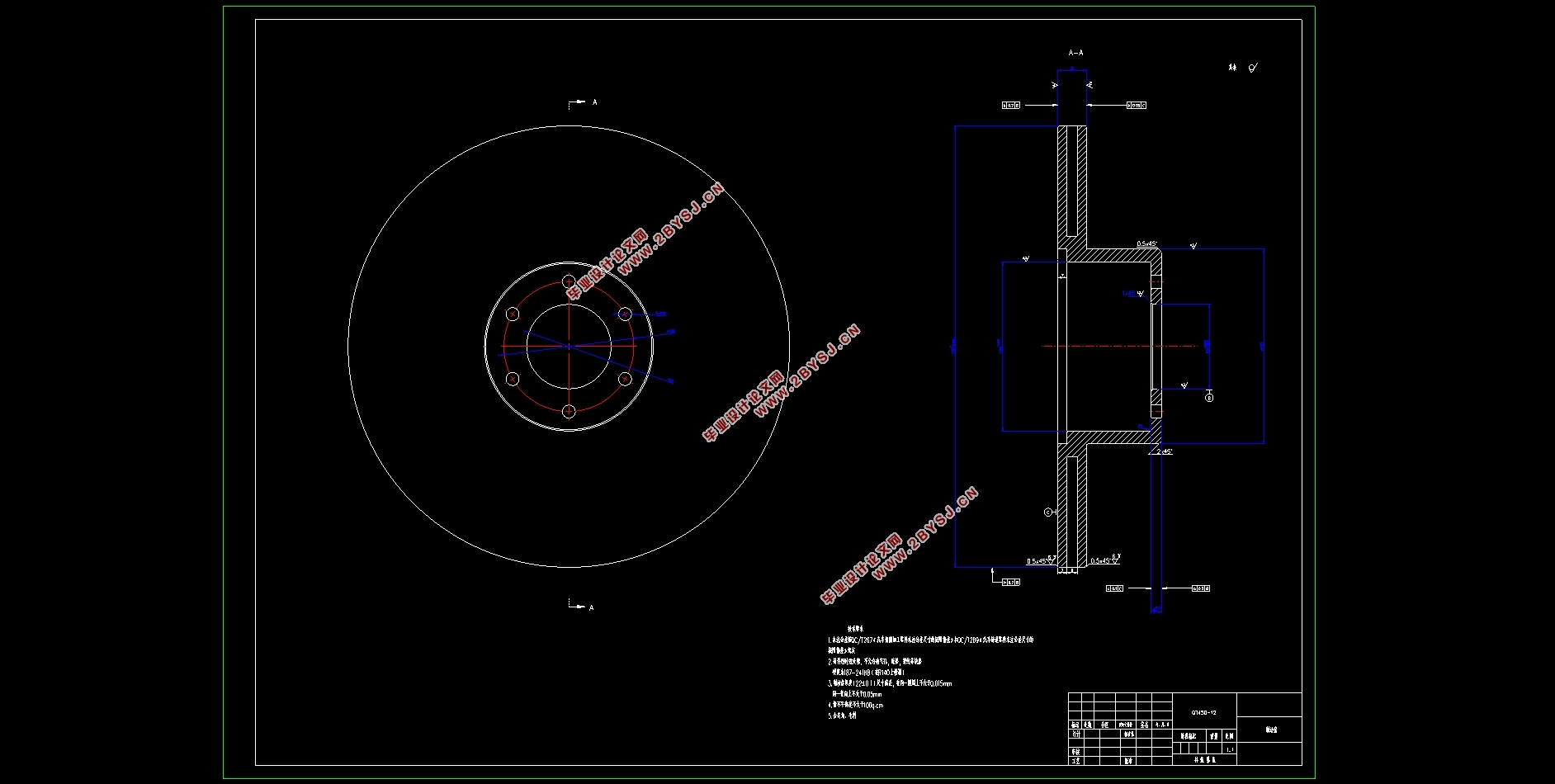
3.2.1 Brake disc 24
(2) Brake disc thickness h 26
3.2.2 Brake block 28
3.2.3 Brake caliper 28
3.2.4 Pad alarm device design 29
3.2.5 Friction material 30
3.2.6 Brake clearance and adjustment 30
3.3 Brake force distribution analysis 31
3.4 Selection of synchronization adhesion coefficient 32
3.5 Brake performance factor 33
3.6 Brake braking torque calculation 34
3.7 Brake system performance requirements 34
3.7.1 Requirements for directional stability of the car during braking 35
3.7.2 Brake deceleration j requirement 36
3.7.3 Braking distance S requirements 36
3.7.4 Brake torque requirements 37
3.7.5 Specific energy dissipation rate requirements for wheel brakes 37
3.7.6 Comparison of friction requirements 37
3.7.7 Requirements for heat flux density 37
3.7.8 Requirements for the absorption power of the pad 37
3.7.9 Average friction requirements 37
3.7.10 The service brake has at least two independent drive lines 37
3.7.11 Prevent water and sludge from entering the brake working surface 38
3.7.12 Requires good thermal stability of braking capability 38
3.7.13 Lightweight operation 39
3.7.14 Calculation of pedal force during emergency braking 39
3.7.15 Brake pedal travel calculation 39
3.7.16 Subsidiary calculation 40
3.8 Friction lining wear characteristics 40
4.1Brake heat capacity and temperature rise accounting 43
4.2 Brake commissioning 44
4.2.1Technical requirements for brake discs 44
4.2.2 Brake caliper technology assembly requirements 44
4.2.3 Hub assembly technical requirements 45
Conclusion 47
References 48
