联合花生收获机的设计与实现(含CAD零件装配图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
联合花生收获机的设计与实现(含CAD零件装配图)(课题申报表,任务书,开题报告,中期检查表,外文翻译,论文说明书15000字,CAD图纸9张,答辩PPT)
Design and implementation of a combined peanut harvester
摘要
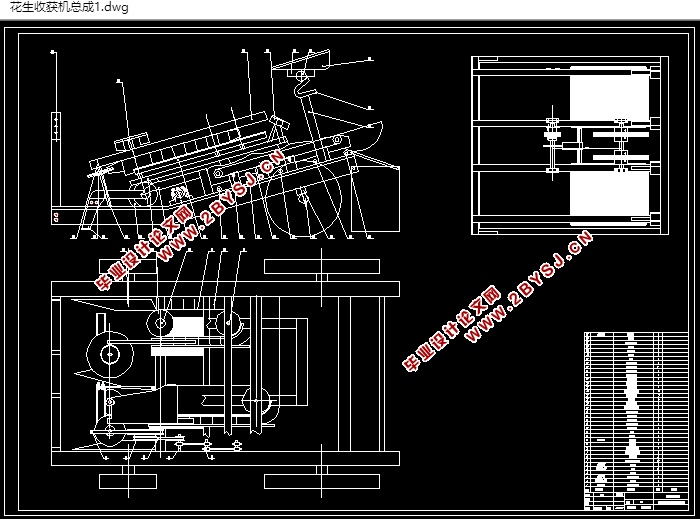
小型联合型花生收获机将两垄花生的藤、荚果和土壤同时犁起,在联合收获系统的作业下,将实现土壤的粉碎、果与藤的分离,在经过清选部件之后,实现花生的完整收获。完整的收获过程为:花生藤的分离扶起,犁耕,取果,土壤粉碎,果藤输送,荚果清选,集果。
根据花生生长的特点和收获技术的要求,小型花生联合收获机具有系统结构精确紧密、机器重量较轻、分离性能好的特点。采用八面碎土齿,首次破碎土壤块时便可使土壤破碎率达75%以上,再经过二次粉碎后,可实现土壤的完全细化。花生荚果被五个抛土轮从土壤中分离出来,摘果刀的刀刃将花生藤与荚果实分离,被传输轮拾取的藤条被收集,由机尾的出藤口排出。花生分离清选出后的果实直接落入荚果收集箱。收获后的花生由于清洁度高可以直接晾晒干燥、转运储存。
由于设计的机械系统较为精简,机器的造价成本的低廉,该花生联合收获机械适合小型家庭农场化的花生种植收获的农业生产,其作业效率与以往的人工采收相比有了显著的提升。
关键词:联合收获;低耗高效;分离彻底;低成本
ABSTRACT
The small combined peanut harvester simultaneously ploughs the vines, pods and soil of two ridge peanuts. Under the operation of the combined harvesting system, the communication of the soil and the separation of the fruit and the vine will be achieved. After the components have been selected, the peanuts will be obtained. Complete harvest. The complete harvesting process is as follows: separation and promotion of peanut vines, plowing, fruit harvesting, soil smashing, fruit vine transport, pod selection, fruit collection.
According to the characteristics of peanut growth and the requirements of harvesting technology, the small peanut combine harvester has the characteristics of precise and compact system structure, lighter machine weight and good separation performance. The use of eight-faced soil scrapers can result in a soil crushing rate of more than 70% when the soil blocks are broken for the first time. After the secondary crushing, complete soil refinement can be achieved. Peanut pods were separated from the soil by five throwing wheels. The blades of the picking knife separated the peanut vines from the pods. The rattan picked up by the transmission wheel was collected and discharged from the tail of the tail. The fruit that is separated from the peanuts is directly dropped into the pod collection box. The peanuts harvested can be directly dried, transported, and stored for cleanliness.
Since the designed mechanical system is relatively simple and the cost of the machine is low, the peanut combined harvesting machine is suitable for small-scale family-farm farmed peanut harvesting and agricultural production, and its operating efficiency has been significantly improved compared to previous manual operations.
Key words: joint harvesting low consumption high efficiency efficient complete separation low cost
收获机系统总体方案
种植的花生与土豆、红薯等果实都在土壤中的作物相比,其每株植株上的荚果多且较小。同时花生收获机械在犁耕翻起植株的效果会受到土地情况的影响,所以在选择方案时应考虑不同的地面土壤情况对采收效率的影响。
花生作为深根系作物之一,对土壤的通气性等要求较高,生长环境沙壤土或沙土的最为适宜,我国种植花生的方法主要有四种,分别为垄作、平作、高畦种植和轮作换茬。大多数地区主要的种植方式为垄作,分为大垄双行和一垄一行两种方法。垄作优势是密植合理,保证田间通风采光,是花生得到高产的必要条件。为一垄一行的种植模式,行距为550mm,株距为160mm。适应大部分地区的种植实际情况。图2-1为花生种植情况的简图。
花生收获机主要工作参数
查阅相关资料得知收获相关参数。
⑴、起耕的深度
一般情况下花生果实在地底100~120mm深度,为保证花生的不漏耕,不落果,将起耕的深度设定在150mm。
⑵、作业行数的选定
随着花生种植技术的发展,地膜覆盖栽培得到普及,这种种植方式全部使用双辛垄种植,垄上的行距是300 mm,垄距一般为500~600 mm,且平作花生的行距是300 mm,所以本设计的选择作业行数为2行。
⑶、作业速度
由于前进速度与挖掘铲所受到的阻力成正比关系,速度越快,所受到的阻力越大,拖拉机提供的牵引力越小,因此综合考虑初定速度为1.2~ 1. 5 km/h。

目 录
1绪论 3
1.1花生种植的分布及种类 3
1.2花生的主要收获方式 4
1.3国内花生收获机械发展研究概况 6
1.4 论文主要研究内容 9
2 收获机系统总体方案 10
2.1结构总体设计原则 10
2.2 花生收获机总系统的确定 11
3 配套动力 13
3.1 花生收获机主要工作参数 13
3.2配套拖拉机的选择 13
3.2.1工作效率的简单计算 14
4 超精型联合花生收获机总体结构与工作原理的设计 15
4.1国内常见的两种花生收获机原理的分析 15
4.2 确定联合花生收获机结构与原理 16
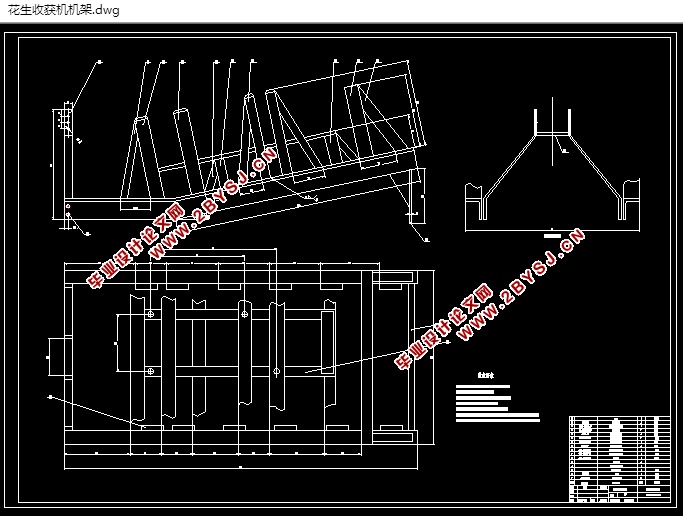
5 相关零部件的结构设计与计算 19
5.1 具体机架结构和制造要求 19
5.1.1 机架的生产要求 19
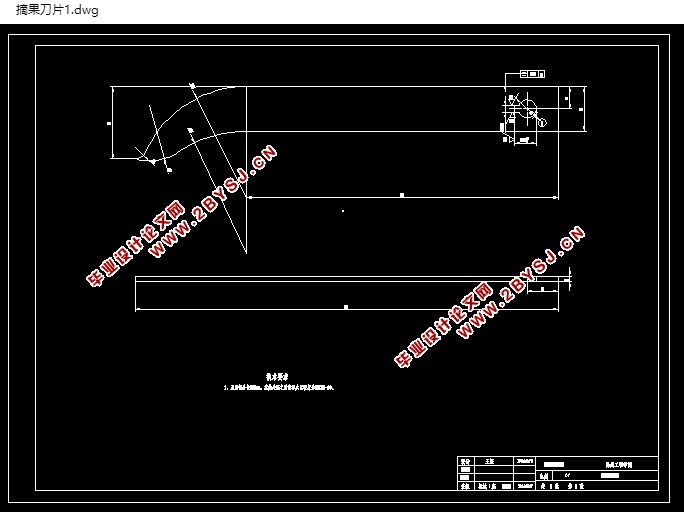
5.2 荚果采摘刀的设计 21
5.3 碎土齿轮的外形及功能要求 22
5.4 挡果盖板结构和简易要求 23
5.5 起耕刀的结构设计 24
5.5.1 起耕刀耕犁时的角度分析 24
5.5.2 起耕刀刀具面的宽度计算 26
6 碎土轮链相关参数的计算 27
6.1.计算传动链轮的相关参数 27
6.2链轮传动的功率Pca 27
6.3传动链条的链接数Lp 27
6.4计算传动链条的链条节距P 28
6.5计算传动链长L及链条中心距a 28
6.6由相关传动链条来设计传动链轮: 29
6.6.1小链轮的计算 29
6.6.2大链轮的计算: 30
6.7 分土轮轴的设计与校验 31
7 其他部分零件的简要说明及技术要求 33
7.1、拔禾器的设计 33
7.2、拔禾轮的作用 33
7.3、上压藤板的设计 33
7.4、输藤带的设计及要求 34
7.5、夹、压藤板的设计及配置 34
7.6、果筛的设计 34
结论 35
致谢 36
参考文献 37
