智能护眼台灯的设计
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
智能护眼台灯的设计(论文12000字)
摘要:传统的台灯大多功能单一, 且控制器一般都是安装在灯臂上,人们必须手动按下控制器才能实现对LED灯开关控制,并且没有坐姿提醒功能。本文设计了一款基于STC89C52单片机的手机控制的LED灯。以单片机作为主控芯片,人体热释红外传感器、红外避障传感器、光照检测电路(光敏电阻)、A/D采样PCF8591电路、电源、蓝牙模块电路等外围设备来实现灯光强度随外界光线变化而自动变化或者熄灭,并在传统的台灯上添加了坐姿提醒、智能控制、人体感应、预防近视等功能,弥补了传统台灯的不足。本设计具较强的实用性,具有节能省电、使用方便、保护眼睛等诸多优点,在实际生活中用处广泛,因此它的设计具有一定的使用价值。
关键词:智能台灯; 传感器; 蓝牙技术; 多功能;
Design of intelligent eye lamp for eye protection
Abstract : Most of the traditional desk lamps have a single function, and the controller is usually installed on the lamp arm. People must press the controller manually to realize the control of the LED light switch, and there is no sitting posture reminding function. This paper designs a LED lamp controlled by mobile phone based on STC89C52 microcontroller. With the MCU as the main control chip, the human body thermoluminescence infrared sensor, infrared obstacle avoidance sensor, light detection circuit (photosensitive resistance), A/D sampling PCF8591 circuit, power supply, Bluetooth module circuit and other peripheral equipment to realize the light intensity change automatically or extinguish with the change of the outside light, and add the sitting on the traditional desk lamp. The functions of posture reminder, intelligent control, human body induction and myopia prevention make up for the shortage of traditional table lamps. The design has strong practicality, has many advantages, such as energy saving, electricity saving, convenient use and eye protection. It is widely used in real life, so its design has a certain value of use.
Key words : Intelligent desk lamp; Sensor; Bluetooth technology; Multi-function;
目 录
1 引言 1
1.1课题背景及其意义 1
1.2 国内外的研究状况 1
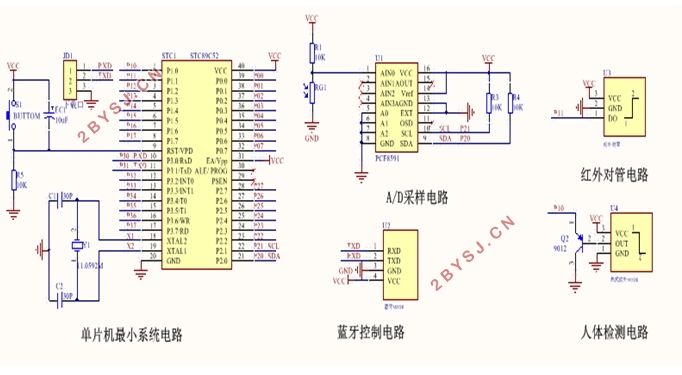
2 硬件电路设计 2
2.1系统总体结构 2
2.2设计方案 3
2.3单片机电路设计 3
2.4电源电路设计 6
2.5光照检测电路设计 6
2.6 A/D采样电路设计 6
2.7照明电路设计 8
2.8蓝牙电路设计 8
2.9测距电路设计 9
2.10 蜂鸣器报警电路设计 11
2.11 红外感应模块电路设计 12
3 软件设计 12
3.1程序总流程图 13
3.2PCB板设计 14
3.3手机APP界面设计 15
4 实物测试与结果分析 15
4.1 硬件电路制作 15
4.2 整体系统调试 15
4.2.1 系统软件调试 15
4.2.2 硬件测试 16
4.3 实物测试 16
5 总结与展望 18
参考文献 19
附录 21
致谢 25
