基于单片机的心率测试仪设计
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
基于单片机的心率测试仪设计(论文13000字)
摘要:心率指标是现代社会评判健康与否的一个重要的指标,是现代医疗检测身体的重要环节。基于单片机的心率测试仪设计不仅仅能够应用于现代的医疗之中,而且可以在日常生活中通过嵌入穿戴设备,做到实时监测,是一项非常具有研究价值和实用性的研究。本课题提出了建立基于单片机基础之上的心率测试仪设计,在首先分析了心率测试仪设计的研究现状的基础上,制定出了心率测试仪的总体设计方案,再次在基于整体设计方案的基础上,确定了具体的实现路径与功能模块,最后,我们通过STM8芯片处理外部传感器所检测到的心率电信号所形成的模拟信号,并将处理后的数据发送至上位机PC端,通过上位机中的LabVIEW来编程,实现心率数值的显示以及心率波形的展现。
关键词:单片机;心率;传感;LabVIEW
Design of heart rate tester based on single chip microcomputer
Abstract: The heart rate index is an important index for modern society to judge whether it is healthy or not. It is an important part of modern medical examination. The design of heart rate tester based on singlechip can not only be used in modern medical treatment, but also can be monitored in real time by embedding wearable equipment in daily life. It is a very valuable and practical research. This subject puts forward the design of heart rate tester based on single chip microcomputer. Based on the analysis of the current research status of the heart rate tester design, the overall design scheme of the heart rate tester is formulated. On the basis of the overall design scheme, the concrete realization path and function module are determined. After that, we deal with the analog signals of the heart rate signal detected by the external sensor by the STM8 chip, and send the processed data to the PC end of the upper computer, and program by LabVIEW in the upper computer to realize the display of heart rate and the display of the heart rate waveform.
Key words: Single chip microcomputer; heart rate; sensor; LabVIEW

目 录
一 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 心率监测设备的研究现状 1
二 心率监测测试仪设计 4
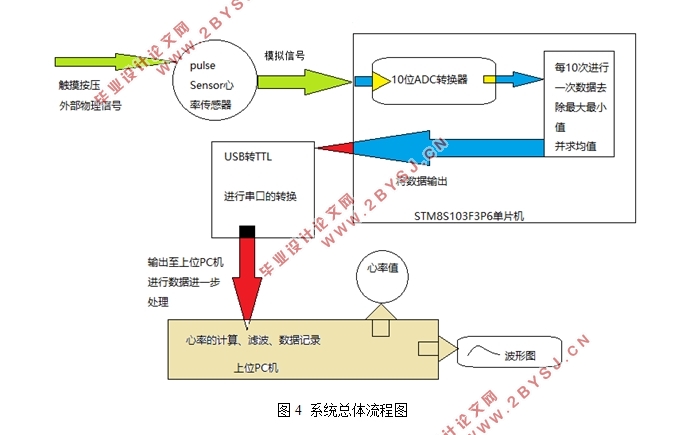
2.1总体设计 4
2.2 硬件的各模块的设计 4
2.2.1 心率传感器模块 5
2.2.2 STM8S103F3P6单片机 7
2.2.3 USB 转 TTL 模块 8
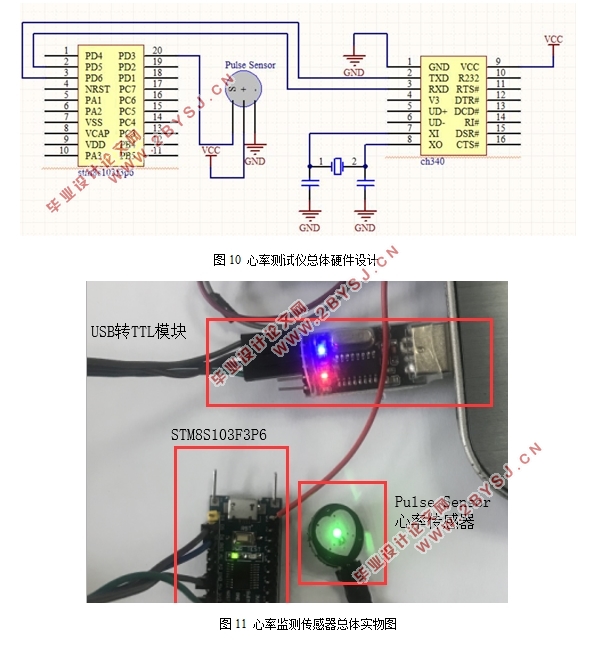
2.2.4 总原理图 9
三 系统软件设计 10
3.1 下位机程序设计 10
3.1.1 IAR For STM8 11
3.1.2 STM8S103F3P6程序设计 12
3.2 上位机程序设计 16
3.2.1 LabVIEW 16
3.2.2 心率计算 18
3.3.3 波形显示 19
四 心率检测传感器的实验分析 22
4.1 心率检测传感器的制作 22
4.1.1 Pulse Sensor心率传感器测试 22
4.1.3 通信测试 22
4.15 总体测试 23
4.2 实验方法设计与安排 23
4.2.1 干扰减弱措施 24
4.2.2 实验方案 25
4.3 实验数据分析 26
五 总结和展望 27
参考文献 29
致谢 30
附录 31
