基于运动控制卡的控制研究(PID控制)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
基于运动控制卡的控制研究(PID算法)(任务书,开题报告,毕业论文17000字)
摘要
现在的社会发展速度很快,传统的加工技术(如人工切削、铸造、人工打磨、钳工等)已经不能满足现代化工业的需求,现代机械加工讲究的是加工速度快、精度高、性能优良、尽量的减少浪费,缩小成本,从中取得最大的利益。机械加工想要在信息进步的时代中站稳自己的脚步,就必须与智能化信息技术相结合。
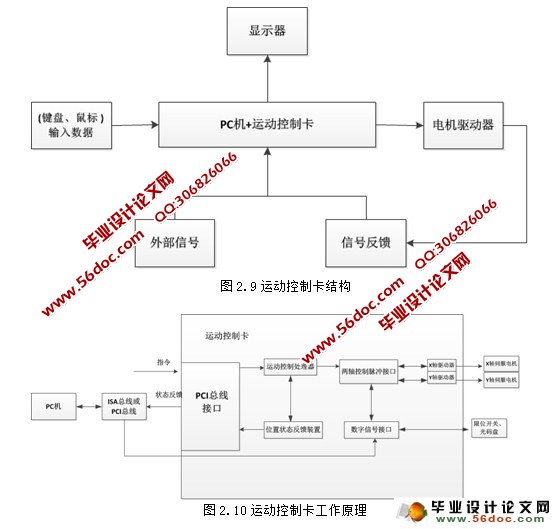
运动控制技术是由多种复杂技术相结合的一个创新,它的出现使得机械工业得到了巨大进步。它主要的核心技术是DSP,在与计算机配合使用的时候,可以直接插进PCI插槽中。运动控制卡内部自身带有开放的数据函数库,使用起来很方便,它相对来说很精确、能力也很强。插补是控制方面最基本的要求,运动控制卡对于插补的满足能力很强,现在被很多行业使用。
本文首先对目前一些机械加工的实际情况进行分析,了解现代技术的发展情况,对一些软硬件的使用、特点等进行分析,并组成了一个与计算机相结合的运动控制卡系统。其次,利用PID控制的一些算法,根据搭建的系统,计算出需要的一些参数,通过实验仿真证明它的可靠性。最后来做插补实验,以体现运动控制卡的精度等特点。
关键词:运动控制;PID;插补
Abstract
With the development of the social economy, the traditional processing technology (such as artificial cutting, casting, grinding, fitter, etc.) can not be satisfied with the needs of modern industry. The modern machinery processing industry is all about processing speed, high precision, good performance, reducing waste, reducing costs and getting the largest interests. Mechanical processing must be combined with intelligent information technology to stand its step in the information time .
Motion control technology is an innovation of the combination of various complex technology. It brings the big advance of mechanical industry. Its main core technology is DSP, which can be directly inserted into the PCI slot when it is used with the computer. As the motion control card has its own data library inside, it is convenient to be used. It is relatively accurate and its ability is very strong. Interpolation is the most basic requirement of controlling, and the motion control card can meet the needs of interpolation fiercely, so it is used by many industry fields.
At first, some actual situations in real life now are analyzed in this paper to understand the development of modern technology. The use and characteristic of some hardware and software are analyzed, and a motion control card system combined with the computer has been formed. Then, the parameters needed are calculated by using some algorithms of PID control according to the system. Its reliability is proved through the experiment simulation. Finally, the interpolation experiment is completed to reflect the precision of the movement control CARDS and other characteristic.
Key words: motion control;PID; interpolation
1.3课题研究目的及内容
1.3.1课题研究目的
上面已经介绍过了运动控制技术的重要性以及运用的广泛程度,虽然现在的运动控制器远远比以往的传统技术、手工制造等更加先进,但是随着社会不断进步,信息技术不断提高,目前的等等,都必须与时俱进,提前开发,以达到人们所需。本文主要是以运动控制卡入手,根据不同的功能、性能等情况选取器部件,从而搭建控制系统。使得系统更加智能、方便;更加符合人们所需要的条件[5]。
1.3.2课题研究内容
本文是以PCI总线的运动控制卡为前提,通过选取器部件搭建控制系统,利用PID控制原理,计算出相应的参数,然后通过实验仿真测试其模块的功能,最后通过设计好的控制系统做一个插补实验,通过对实验的分析,找出问题并改善。本文共分为五个部分,各部分内容如下:
第一章:绪论。
第二章:控制系统的硬件分析
第三章:PID控制及仿真
第四章:插补分析和实验总结
第五章:结论

目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 - 1 -
1.1课题背景 - 1 -
1.1.1直线电机驱动技术 - 1 -
1.1.2可编程控制器 - 1 -
1.1.3运动控制卡 - 2 -
1.2运动控制卡的发展和研究 - 2 -
1.3课题研究目的及内容 - 3 -
1.3.1课题研究目的 - 3 -
1.3.2课题研究内容 - 3 -
第2章 控制系统的硬件分析 - 4 -
2.1控制技术的分析 - 4 -
2.1.1单片机的特点及应用 - 4 -
2.1.2可编程控制器的特点及应用 - 5 -
2.1.2.1 PLC的特点 - 6 -
2.1.2.2 PLC的缺陷 - 7 -
2.1.2.3 PLC的应用 - 8 -
2.1.3运动控制卡的特点及应用 - 8 -
2.1.3.1 运动控制卡的特点 - 10 -
2.1.3.2 运动控制卡的应用 - 10 -
2.1.4控制技术的选定 - 11 -
2.2传感器的选型 - 11 -
2.2.1传感器及其组成 - 11 -
2.2.1.1传感器的定义 - 11 -
2.2.1.2传感器的构成 - 11 -
2.2.2传感器的特性 - 11 -
2.2.3传感器的分类 - 13 -
2.2.3.1常用传感器的原理及应用 - 13 -
2.2.3.2现代新型传感器 - 14 -
2.2.3.3一般传感器的选择 - 14 -
2.2.4传感器的选型 - 15 -
2.3步进电机和驱动器 - 19 -
2.3.1步进电动机的工作原理 - 19 -
2.3.2步进电动机的重要参数 - 19 -
2.3.3步进电机的分类 - 21 -
2.3.4步进电机和驱动器选型 - 22 -
2.4 本章小结 - 24 -
第三章 PID控制系统 - 25 -
3.1 PID控制系统的发展及现状 - 25 -
3.2 PID控制的算法 - 25 -
3.2.1 PID控制原理 - 25 -
3.2.2 PID算法 - 25 -
3.3 PID控制仿真 - 27 -
3.3.1 PID控制器的传递函数 - 27 -
3.3.2 Simulink建模 - 28 -
3.3.3 实验仿真及总结 - 30 -
3.4 本章小结 - 37 -
第四章 插补实验 - 38 -
4.1 插补原理 - 38 -
4.2 插补分析和实验仿真 - 38 -
4.2.1 逐点比较法直线插补 - 38 -
4.2.1.1插补原理 - 38 -
4.2.1.2插补实验 - 40 -
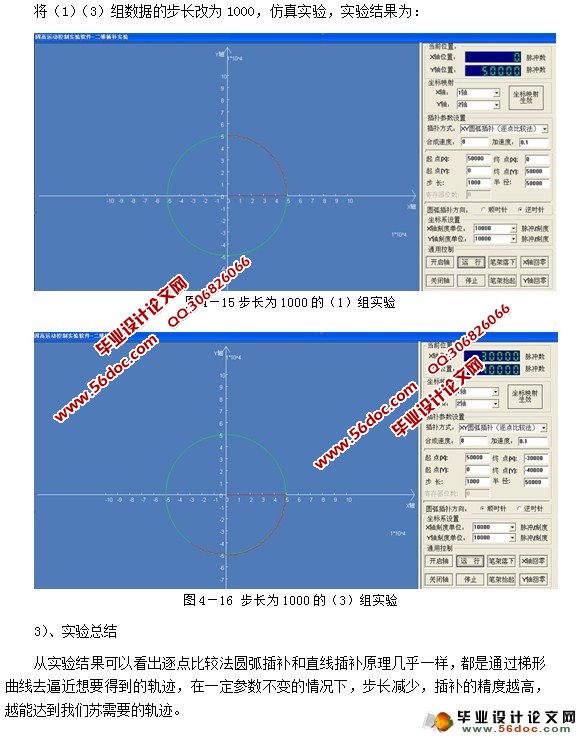
4.2.2 逐点比较法圆弧插补 - 43 -
4.2.2.1插补原理 - 43 -
4.2.2.2插补实验 - 44 -
4.3 本章小结 - 47 -
结论 - 49 -
参考文献 - 50 -
致谢 - 53 -
