基于单片机的太阳能充电器设计(含电路图,Proteus仿真程序)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
基于单片机的太阳能充电器设计(含电路图,Proteus仿真程序)(论文13000字,Proteus仿真程序)
摘要
随着我国经济的快速发展,促使各种能源使用入不敷出。太阳能作为能源的一种也备受人们关注,尤其体现在太阳能发电技术,在这项技术中太阳板受光面与太阳光线的角度是决定太阳能发电效率的关键因素。
本文利用STC89S52单片机设计一款太阳能充电器的控制系统,通过对光敏电阻的输出值进行采集,控制步进电机转动,带动电池板向光照强的方向转动,使得太阳能电池板获得最大的发电功率。通过对电压传感器和电流传感器的检测,当检测充电电压和电流大设置值时,自动断开充电电路。
本设计由软件和硬件两部分组成,硬件设计对单片机最小系统、电压电流采集电路、充电控制电路、按键电路、液晶显示电路、报警电路等进行设计,使控制器具备电压、电流检测,系统参数显示,自动断电控制等功能;软件设计方面对控制器的软件驱动程序进行设计。并利用Protues软件进行可行性仿真,对软件和硬件设计进行验证。
关键词 光敏电阻;单片机;太阳跟踪;步进电机
Abstract
With the rapid development of economy in our country, various energy use to make ends meet. Solar energy as a kind of is people's attention, particularly in solar technology, solar panels in the technology receives from the perspective of the sun's rays is the key factor that decide the efficiency of solar power.
Using STC89S52 microcontroller design a solar charger control system, through the acquisition of the output value of photosensitive resistance, control of stepping motor rotation, led panels turn towards the direction of the light is strong, make solar panels for maximum power. Through the voltage sensor and current sensor test, when detecting large charging voltage and current setting, automatic disconnect charging circuit.
This design consists of two parts, software and hardware, the hardware design of single chip microcomputer minimum system, voltage charging electric current sampling circuit, control circuit, key circuit, liquid crystal display circuit, alarm circuit and so on to carry on the design, make the controller have voltage, current, the system parameter display, automatic power control; The software design in the face of the software driver to carry on the design of the controller. And the feasibility of using Protues software simulation, the software and hardware design for validation.
Keywords Photosensitive resistance Single chip microcomputer Sun tracking Stepping motor
2.1设计目标
(1)实现对36V蓄电池的充电。
(2)实现对充电电压、电流和电池电压和电流的检测功能。
(3)实时显示充电压、电流和电池电压、电池的实时显示。
(4)完成太阳能最大功率跟踪系统的软件和硬件设计。
2.2设计思想
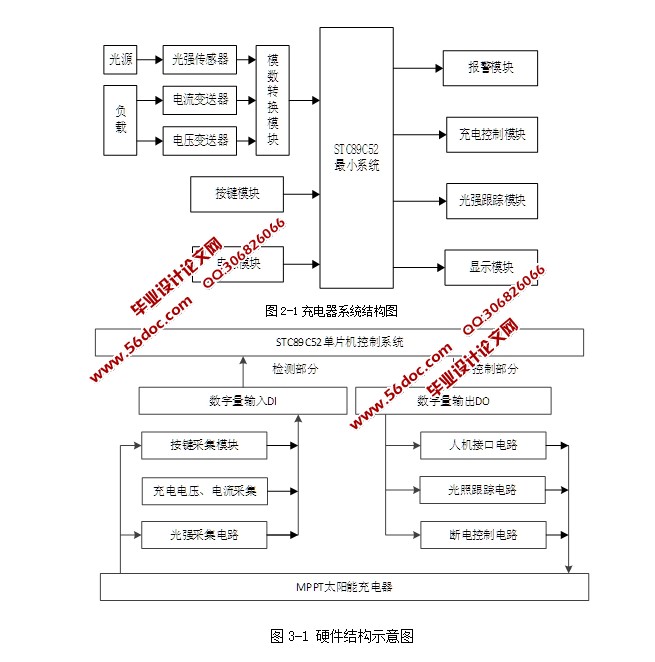
根据系统目标可知,系统需要实现输入的采集功能(按键、充电电压、充电电流、蓄电池电压、蓄电池电流、光照轻度的采集)和输出(液晶显示、蜂鸣器报警)的控制功能。通过对整体设计目标进行评估设计中选择单片机作为核心的控制芯片,通过扩展电压、电流采集电路、光强采集、蜂鸣器报警电路、液晶显示电路、按键电路等接口电路实现系统硬件设计。通过软件编程控制各个功能模块协调工作,完成太阳能充电器的设计要求。
2.2系统框架
系统由单片机最小系统,按键电路,传感器采集电路、液晶显示电路、报警电路、充电控制电路、显示电路、电源电路、光强跟踪电路组成。


目 录
1 绪论 1
1.1 设计背景及意义 1
1.2 太阳能的发展现状 1
1.2.1 太阳能的发展现状 1
1.2.2太阳能的发展前景 1
1.3 本文研究内容及结构安排 3
2 系统的总体设计 4
2.1设计目标 4
2.2设计思想 4
2.2系统框架 4
2.3系统方案论证 4
2.3.1太阳能跟踪方案论证 4
2.3.2主控器选型论证 5
2.3.3传感器选型论证 6
2.4本章小结 6
3 系统硬件设计 7
3.1单片机最小系统 8
3.1.1 单片机最小系统 8
3.2光强检测电路设计 8
3.2.1光强检测电路原理 8
3.2.2光强检测电路模块设计 9
3.3光强跟踪电路设计 10
3.3.1步进电机的介绍及选用 10
3.3.2步进电机驱动电路设计 10
3.4 充电控制电路 11
3.5传感器采集电路设计 11
3.5.1电流变送器介绍 11
3.5.2传感器采集电路设计 12
3.6显示电路设计 13
3.7按键电路设计 13
3.8充电控制电路设计 13
3.9报警电路设计 14
3.10本章小节 14
4 系统软件设计 15
4.1主程序设计 15
4.2电机控制子程序设计 16
4.3充电界面显示子程序设计 17
4.4设置目标充电电压子程序 18
4.5设置目标充电电流子程序 19
4.6本章小结 19
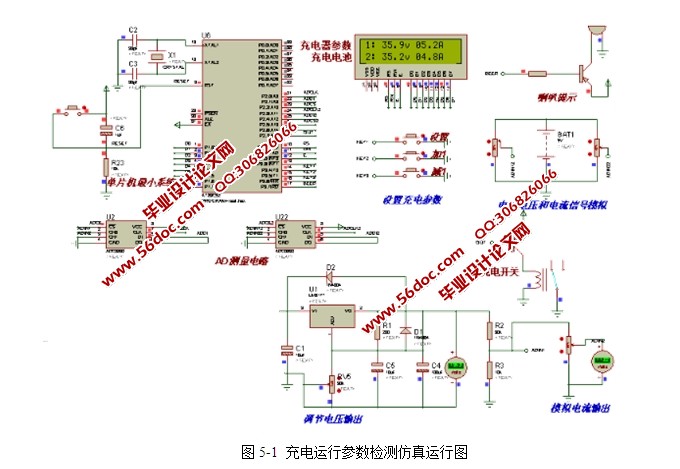
5 系统仿真 20
5.1仿真软件介绍 20
5.2仿真建立步骤 20
5.3仿真原理介绍 20
5.4仿真运行结果分析 21
结论 23
致谢 24
参考文献 25
