BM850T立式加工中心电气控制系统设计(含CAD图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
BM850T立式加工中心电气控制系统设计(含CAD图)(任务书,设计说明书12000字,CAD图纸17张)
摘要
数控技术发展飞速的今天,数控技术在现代制造业发挥越来越重要的作用,数控机床是数控制造业的核心,随着国际国内经济的迅猛发展,机床工业也有了飞跃的发展:体现在新技术的广泛应用和企业效益的明显改善。目前机床行业的消费主流是数控机床。从国内外市场对数控机床的需求来看,以后数控机床市场具有以下特征:一是经济型数控机床是以后的主流产品。二采用新技术,降低成本,提高产品稳定性是企业生存的关键。本文主要介绍了对数控铣床的电气系统设计的过程。
立式加工数控铣削版,对其电气系统设计是尤为重要的,其内容包括进行立式加工中心强电系统设计,PLC部分的电气控制系统设计,伺服驱动系统的选型和电气控制系统设计。
本设计给出了整个数字电气控制系统的电路图绘制,重点部分模块化,较详细地介绍了各个部分的功能及用途。分为808D数控系统设计,电源分配电路,直流和交流控制电路,伺服电源电路,急停控制电路,工件照明电路设计,电气元件选择,伺服驱动器、伺服电机的选择,电气线路的连接与调试,常见连接故障处理。
通过本设计说明书可以基本上掌握立式加工数控铣床的电气原理,以及基本的电气常识,使读者无论是从整体上还是各个模块中都能够了解到数控铣床相关的一系列电气知识。
关键词: 数控系统; 数控铣床; 主电路; 控制电路; PLC控制;电气原理图
Abstract
Numerical control technology rapid development today, the numerical control technology play more and more important role in modern manufactuiring, numerical control machine tool is the core of the numerical control manufacturing, with the rapid development of international and domestic economy, the machine tool industry has a leap in the development, reflected in the wide application of new technology and enterprise efficiency improved significantly. The machine tool industry mainstream consumption is no machine tools. From domestic and international market demand for CNC machine tools, CNC machine after the market has the following characteristics: one is the economical no machine tool is the mainstream products later. 2 adopt new technology, reduce costs, improve product, stability is the key of enterprise survival. This article mainly introduced the process of CNC milling machine electrical system design.
Vertical no milling machining, the electrical system design is particularly important, its content includes system design, vertical machining center part of PLC electrical control system design, selection of servo drive system and electric control system design. This design gives the whole circuit diagram drawing of digital electrical control system, the key part of modular, introduces in detail the function and usuage of the parts. Is divided into 808 d numerical control system design, power distribution circuit, do and at control circuit, servo power circuit, stop control circuit, and artifacts ligheing circuit design, electrical components selection, the choice of servo driver, servo motor, electrical wiring connection and debugging, fault handling common connection.
Through this design manual can basically grasp the vertical processing electrical principle of CNC milling machine, as well as the basic electrical sense, make readers both as a whole and each module can be realized in the CNC milling machine, a series of electrical knowledge.
Key words: CNC system; CNC milling machine; Main circuit; Control circuit; PLC control; Electrical schematic diagram
数控系统选择Siumerik 808D铣削版。进行立式加工中心强电系统设计,PLC部分的电气控制系统设计,伺服驱动系统的选型和电气控制系统设计。主要技术参数:主轴电机功率7.5KW,主轴最高转速6000r/min,进给部分功率6.0KW,冷却功率0.4KW,排屑电动机功率0.4KW,电源总容量18KVA。
毕业设计(论文)专题部分:
(1)数控系统选型:选择Siumerik 808D 铣削版。(2)立式加工中心强电系统设计:电源分配电路,直流和交流控制电路,伺服电源电路。(3)PLC 部分的电气控制系统设计:I/O 地址分配,I/O电路设计,电气元件选择。(4)伺服驱动器、伺服电机的选择,与CNC系统的电气连接电路设计。(5)电气线路的连接与调试,常见连接故障处理。


目 录
第一章 绪论…………………………………………… 1
1.1 引言 ……………………………………………… 1
1.2 数控机床概述 …………………………………… 1
1.3 数控技术的发展趋势 …………………………… 4
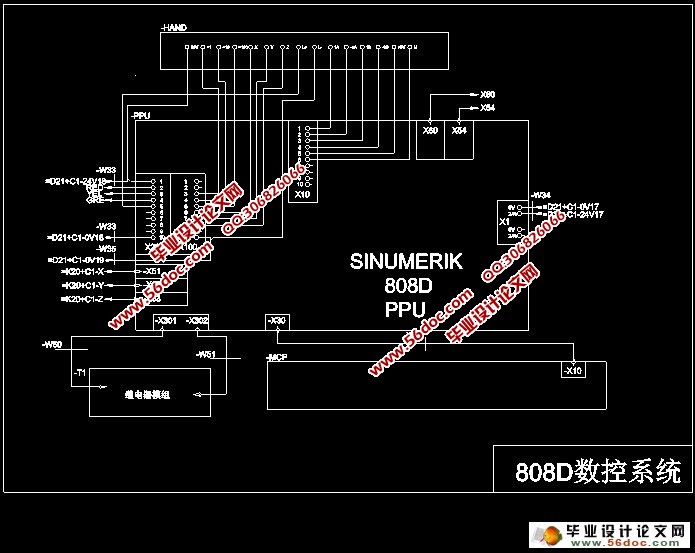
1.4 SINUMERIK 808D ………………………………… 4
第二章 数控系统设计原理…………………………… 5
2.1 数控系统的供电 ………………………………… 5
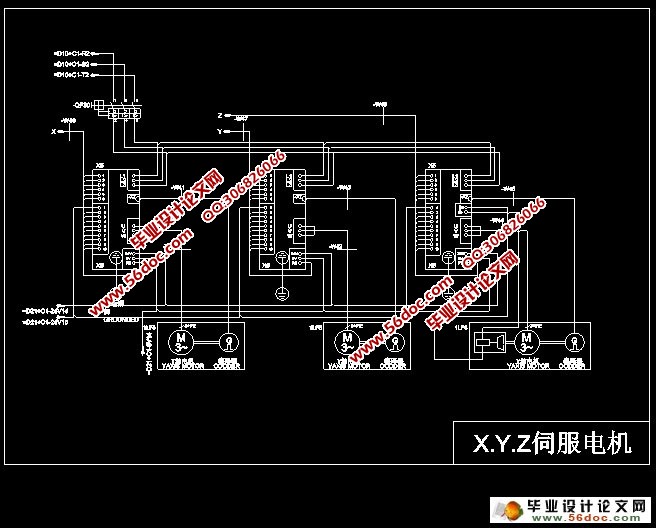
2.2 伺服控制系统电气控制线路设计 ……………… 5
2.3 主轴控制系统电气控制线路设计 ……………… 6
2.3.1 单极性主轴 ………………………………… 6
2.3.2 双极性主轴 ………………………………… 6
2.4 其他辅助功能的电气控制线路设计 …………… 6
第三章 SINUMERIK 808D 组成及电路……………… 8
3.1 三相电源引入 …………………………………… 8
3.3 排屑系统控制 …………………………………… 10
3.3 斗笠式刀库控制 ………………………………… 11
3.4 机床照明温度控制 ……………………………… 14
3.5 润滑控制 ………………………………………… 15
3.6 主轴驱动 ………………………………………… 17
3.7 伺服系统轴驱动控制 …………………………… 18
3.8 行程开关 ………………………………………… 18
3.9 808D 数控系统 ………………………………… 20
第四章 电气数控系统主轴驱动……………………… 21
4.1 机构方式以及选型 ……………………………… 21
4.1.1 电动机 ……………………………………… 21
4.1.2 电动机玄星条件 …………………………… 21
4.1.3 电动机选型 ………………………………… 22
4.2 变频器电动机主轴驱动装置 …………………… 22
4.2.1 设备的选型方法 …………………………… 22
4.2.2 变频器主轴伺服驱动电路 ………………… 23
第五章 系统各部分元器件选型……………………… 24
5.1 低压电器选择及遵从的原则 …………………… 24
5.2 断路器选择标准 ………………………………… 24
5.3 自动开关的选择¬¬¬——保护装置 ………………… 25
5.4 接触器的选择 …………………………………… 25
5.5 热继电器的选择 ………………………………… 25
5.6 中间继电器的选择 ……………………………… 26
结论………………………………………………………… 27
参考文献…………………………………………………… 28
致谢………………………………………………………… 29
