大型车上下车自动伸缩脚踏板的设计(含CAD零件图装配图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
大型车上下车自动伸缩脚踏板的设计(含CAD零件图装配图)(论文说明书9000字,CAD图5张)
摘要
对于大中型车辆来说,过高的底盘使人们上下车会有一定的困难。而车辆踏板的设置会消除上下车困难的同时,也会使车辆不美观,且车辆宽度额外增加。为了改进车辆的这一特点,市场上出现了电动式自动伸缩脚踏板。这种踏板通过电机来控制,通常为平板式或者四连杆式结构。当车辆检测到车门打开时,意味着乘员准备上下车动作。这样,踏板处的电机就会收到来自控制器的信号。踏板处的电机开始工作,将电动脚踏板自动伸出,待乘员完成上下车动作,并且将车门关闭时。车辆收到这一信号,通过控制电机,将自动踏板进行收回。本文主要对自动伸缩式踏板的电机选型,结构分析,主要零部件校核进行一个系统的计算与说明。
关键词:大型车、伸缩、脚踏板、电动化
ABSTRACT
For large and medium-sized vehicles, the excessively high chassis makes it difficult for people to get on and off the vehicle. The setting of vehicle pedals will not only eliminate the difficulty of getting on and off, but also make the vehicle unattractive and increase the width of the vehicle. In order to improve this feature of vehicles, electric automatic telescopic foot pedals have emerged in the market. This type of pedal is controlled by an electric motor, usually in a flat or four link structure. When the vehicle detects that the door is open, it means that the passenger is ready to get on and off the vehicle. In this way, the motor at the pedal will receive a signal from the controller. The motor at the pedal starts working, automatically extending the electric pedal until the passenger completes the boarding and alighting motion and closes the door. The vehicle receives this signal and retracts the automatic pedal by controlling the motor. This article mainly provides a systematic calculation and explanation of the motor selection, structural analysis, and main component verification of the automatic telescopic pedal.
Keywords: large cars, telescopes, pedals, electrification
设计要求
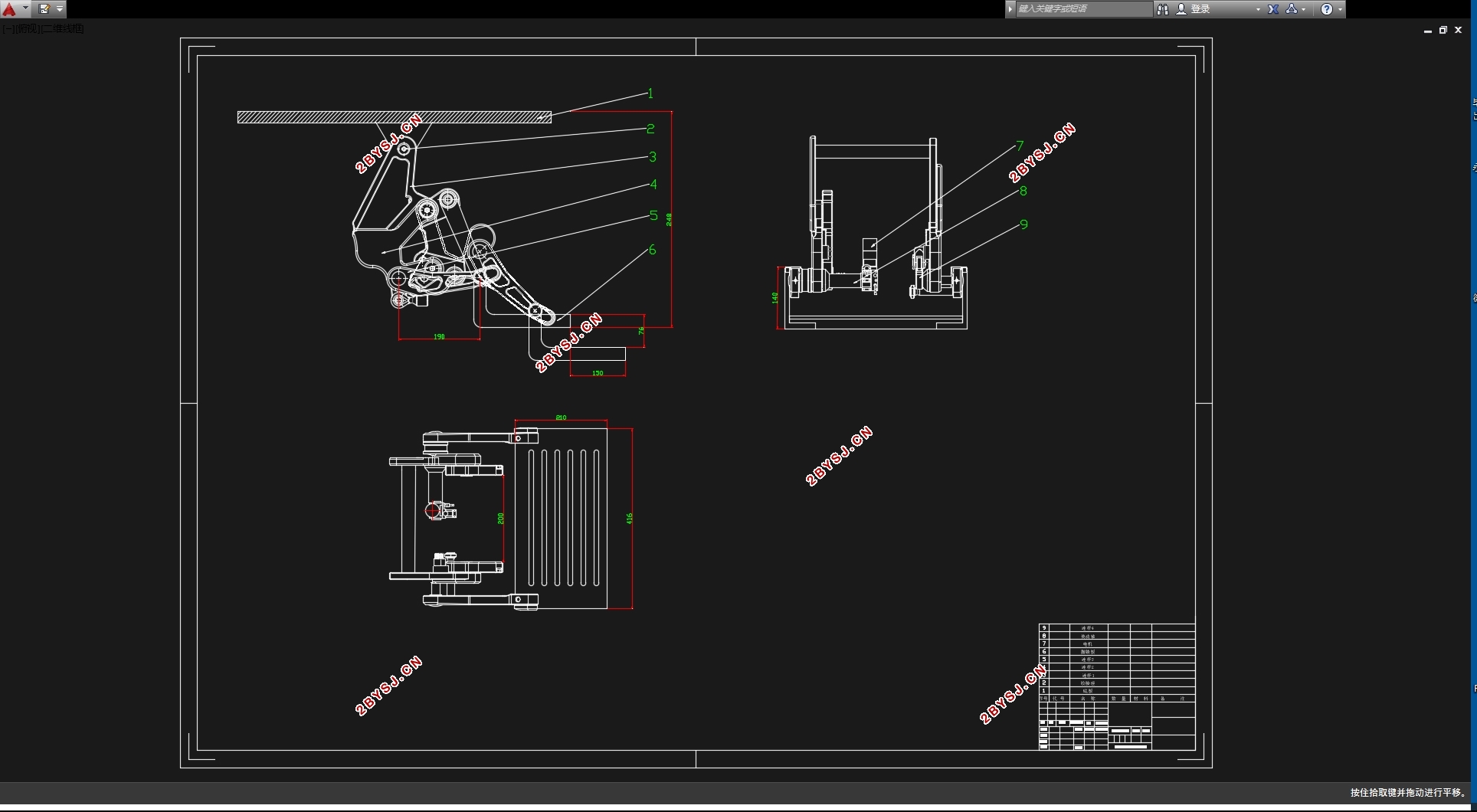
本次设计的四连杆自动升降伸缩式电动脚踏板,所需要的主要参数是:
可承受重力: 200Kg
.踏板伸缩距离要求满足从缩回位置到伸出位置之间长度为130mm。
踏板升降的高度需满足从缩回位置到伸出位置下降70mm。
满足轻量化设计,耐磨耐腐蚀
四连杆机构
电动伸缩踏板采用直流电机驱动,采用四连杆调节踏板姿态,结构设计符合人体工程学原理。主要包括动力机构、传动机构和伸缩机构等。


目录
摘要 1
ABSTRACT 2
第一章绪论 4
1.1引言 4
1.2国内外发展现状 6
1.3主要研究内容 7
第二章总体设计方案 9
2.1设计要求 9
2.2设计方案 9
第三章机械结构设计 10
3.1电机与减速器校核计算 10
3.2选择传动机构类型 13
3.3传动装置总传动比和分配各级传动比 13
3.4计算传动装置的运动和动力参数 13
第四章关键零部件的设计与校核 15
4.1选择齿轮材料、热处理、齿面硬度、精度等级及齿数 15
4.2按齿面接触疲劳强度设计 15
4.3确定齿轮传动主要参数和几何尺寸 17
4.4校核齿根弯曲疲劳强度 17
4.5轴的功用 18
4.6高速轴的设计 18
4.7低速轴的设计 22
总结 26
致谢 27
参考文献 28
