流量为270t/h水-油浮头式换热器(含CAD零件装配图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
流量为270t/h水-油浮头式换热器(含CAD零件装配图)(设计说明书10700字,CAD图纸11张)
摘要
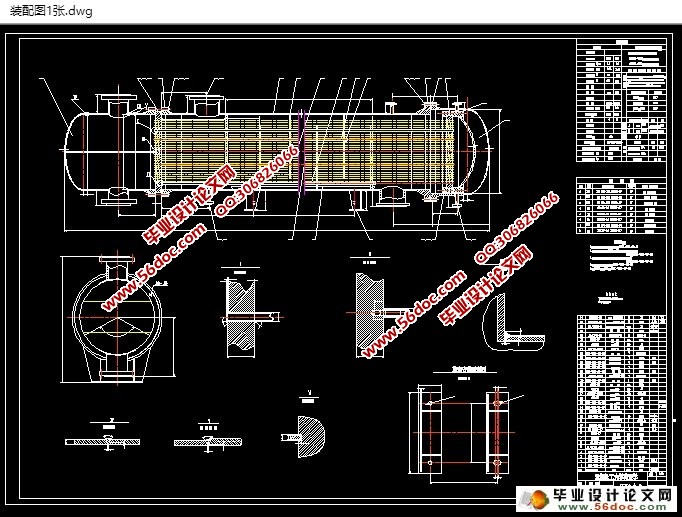
随着经济的发展,各种不同型式和种类的换热器发展很快。浮头式换热器是作为一种广泛应用于石油、化工、食品、动力和原子能等工业部门的换热设备,尤其是在化工机械领域有着重要的意义。在工业生产中,常常用作把低温流体加热或者把高温流体冷却,把液体汽化成蒸汽或者把蒸汽冷凝成液体。换热器既可是一种单元设备,如加热器、冷却器和凝汽器等;换热设备的主要作用是使热量相互传送,使温度达到工艺过程规定的标准,以满足工艺过程的需要。换热器中的管壳式换热器是目前应用最为广泛的一种换热设备,已作为一种标准换热设备。本次的设计为浮头式换热器,浮头式换热器主要是由管箱、管板、壳体、折流板、换热管、拉杆、钩圈、定距管、浮头盖等组成。浮头换热器的一端是管板与壳体固定,另一端为浮动的管板。因此其优点为热应力比较小,于检查,清洗。缺点为结构比较复杂。
本次换热器设计的壳程介质为水,管程介质为油。流量为270t/h,壳程的工作温度为180℃,管程的工作温度为100℃。本次设计主要分为两个部分,第一部分传热工艺的计算,第二部分强度的计算。在传热计算工艺中,包括有传热面积的计算,传热量、传热系数的确定和换热器内径以及换热管型号的选择,以及传热系数、压降及壁温的验算等等问题。在强度计算中主要讨论的有筒体、管箱、封头、管板厚度计算及折流板、法兰、垫片和接管、支座、分隔板等零部件的设计,安装,组合,还要进行一些强度校核。本设计是按照 GB151《管壳式换热器》和 GB150《钢制压力容器》设计的。换热器在工、农业的各个领域应用十分广泛,在日常生活中传热设备也随处可见,是不可能缺少的工艺设备之一。随着研究的深入,工业上的应用也取得了惊人的成果。
随着社会的进步与科技的发展,换热器的设计技术也在不断的更新,现有的科研成果以后的前景必将更加美好,给生活带来了很大的方便。换热器作为传热设备随处可见,在工业中应用尤为普遍,特别是耗能用量非常大的领域,随着节能技术的快速发展,换热器的种类开发也越来越多。换热器是在化学、石油化学及石油炼制工业以及其他一些行业中普遍使用的热量交换设备,它不仅可以单独作为加热器、冷却器使用,而且是一些化工单元操作的重要附属设备,因此在化工生产中也占有非常重要的地位。
关键词: 浮头式换热器; 换热管; 加热器
Abstract
This design mainly discussed heat principles , and heat calculation and heat parameters ,the heat characteristic and heat calculation and heat parameters ,the structure and the size under the given conditions. In industrial production, the main effect of heat exchange equipment is made by high temperature heat fluid is passed to the lower temperature of fluid, the fluid temperature can reach the indexes of the process regulation, in order to meet the needs of the process on . In the heat exchanger tube and shell heat exchanger is the most widely used, a heat exchange equipment has as a standard heat exchange equipment. This design is floating head heat exchanger, it is made up of tube box 、tube sheet、shell、heat exchange tube、baffle plate、draw bar、spacer pipe、hook circle、floating head cover and so on. One tube sheet of the exchanger is connected with shell, and the other tube sheet is floating tube sheet. So it’s easy to check and clean. On the other hand the structure of it complex.
The shell side of heat exchanger design medium for water, in the medium passes for oil. The shell side of the flow rate of 270 t/h, the working temperature is 180℃, monitor the working temperature is 100℃. In eight pieces of baffle are installed on the structure, to increase the turbulence velocity of the fluid. The diameter of the baffle plate is usually 0.2-1.0 times the diameter of shell. Nozzle flange all choose plate flat welding flange, choose saddle support, this design mainly is divided into two parts, one part is heat transfer process calculation, the other part is the strength calculation.
In the process of heat transfer calculation, include area computation 、capacity of heat transmission 、 the determine of heat transfer coefficient and the choice of the heat exchange tube. About strength calculation, it involve the calculating of shell、tube box、sealing head and so on. Heat exchanger is one of the indispensable process equipment. With the deepening of the research, industrial application made remarkable achievements.
With the social progress and technological development.Heat exchanger design techniques are constantly updated.The exsting scientific reseach for my life is a big convenience.The prospects for the future will be more beautiful.As heat exchanger equipment can be seen everywhere, the most widely used in industry, especially in energy consumption is very large areas, with the rapid development of energy-saving technology, heat exchanger type development more and more. Heat exchanger is a chemical, petrochemical and oil refining industry and other industries widely used in heat exchange equipment, it not only can be used as a heater, cooler separately, and some important auxiliary equipment of chemical unit operations, thus occupies very important position in the chemical production.
Key words: Floating head type heat exchange; Heat exchange tube; heater; cooler

目 录
第一章换热器的工艺计算 1
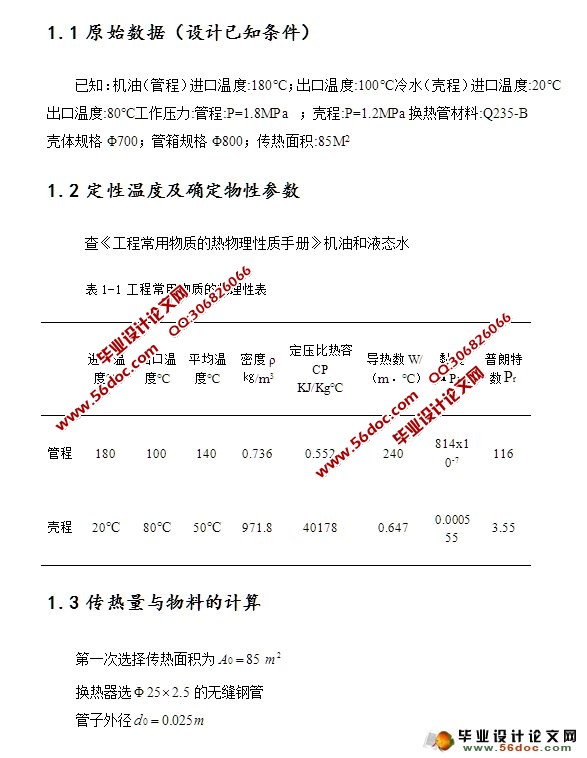
1.1 原始数据(设计已知条件) 1
1.2 定性温度及确定物性参数 1
1.3 传热量与物料的计算 2
1.4 有效平均温差的计算 2
1.5 管程结构初步设计 3
1.6 壳程换热系数的计算 3
1.7 传热系数的计算 4
1.8 管壁温度的计算 4
1.9 管程压降的计算 5
1.10 壳程压降的计算 5
第二章结构设计 7
2.1 换热管材料及规格的选择和根数的确定 7
2.2 布管方式的选择 7
2.3 筒体内径的确定 7
2.4 筒体壁厚的确定 8
2.5 筒体水压试验 10
2.6 管箱侧封头厚度的确定 10
2.7 浮头侧封头厚度的确定 11
2.8 设备法兰的选择 12
2.9 管箱侧法兰的选择 12
2.10 浮头侧法兰的选择 13
2.11 接管法兰的选择 13
2.12 浮头换热器管板的设计计算 14
2.13 浮头设计计算 16
2.13.1 管程压力(内压)作用下浮头盖的计算 16
2.13.2 壳程压力(外压)作用下浮头盖的计算 17
2.13.3 管程压力作用下浮头法兰的计算 17
2.13.4 壳程压力作用下浮头法兰的计算 20
2.14 钩圈的选择 22
2.15 浮动管板的选择 22
2.16 折流板的选择 23
2.17 管箱短节壁厚计算 23
2.18管程与壳程短节的计算 23
2.19 防冲板的选择 24
2.20 接管及开孔补强 24
2.21 支座的选择 25
2.21.1 轴向应力校核 26
2.21.2 切向切应力校核 27
2.21.3 周向应力校核 27
2.21.4 鞍座腹板应力 27
参考文献 28
致谢 29
