自动换刀机械手设计(三维Proe)☆
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
摘 要
加工中心是指在一次装卡中,能够实现自动铣削、钻孔、镗孔、铰孔、攻丝等多工序的数控机床。更为明确的说法是:加工中心就是自动换刀数控镗铣床。这就把加工中心和自动换刀数控车床和车削中心区别开来。
加工中心区别于别的数控镗铣床的主要特点就在于它具有根据工艺要求自动更换所需刀具的功能,机自动换刀(ATC)机能。
加工中心的自动换刀系统,通常是由刀库和机械手组成,它是加工中心的象征,又是加工中心成败的关键环节。因此各加工中心制造厂家都在下大力研制动作迅速、可靠性高的自动换刀装置,以求在激烈的竞争中取得好的效益。正因为自动换刀装置是加工中心的核心内容,各厂家都在保密,极少公开有关资料,尤其机械手部分更始如此。
加重中心的自动换刀形式,可分为有机械手换刀方式和无机械手换刀方式。加工中心的ATC,大都采用有机械手的换刀方式,因为更节省时间。
由于液压驱动的机械手需要采用严格的密封,还需较复杂的缓冲机构,控制机械手动作的电磁阀都有一定的时间常数,因为换刀速度较慢。近年来国内、外先后研制出凸轮联动式单臂双抓机械手。这种机械手的优点是由电机驱动,不需要较复杂的液压系统及其密封、缓冲机构,没有漏油现象,结构简单,工作可靠。同时,机械手手臂的回转和插刀、拔刀的分解动作是联动的,部分时间可重叠,从而大大缩短了换刀时间。
关键词:机械手;加工中心;自动换刀
Abstract
Machining Center is installed in a card, to achieve automatic milling, drilling, boring, Reaming, Tapping and other processes of CNC machine tools. A more explicit statement of Machining Center is the automatic tool change CNC milling machines. This brings the processing center and automatic tool change CNC lathe and turning centers to distinguish.
Machining Center is different from other CNC milling machines to the main features is that it has under the technological requirements for automatic tool change function, Automatic Tool Change (ATC) function.
Machining Center, ATC system is usually a knife and the composition manipulator, it is a symbol of the processing center. Machining Center is the key to success. Therefore the processing center manufacturers are vigorously developing the next moves quickly, high reliability, ATC, to the fierce competition to achieve good results。It is precisely because of automatic tool change is the core processing center, the manufacturers are confidential, rarely disclose the information In particular, some manipulator so start anew.
Add to the automatic tool change form, it can be divided into a manipulator tool change and free manipulator ATC way. ATC machining centers, most using a manipulator tool change, because it is more time-saving.
Due to hydraulic-driven manipulators need strict sealed need more complex buffer, manipulator control of the solenoid valve moves have a certain amount of time constants, because slower speed up the pace. In recent years, domestic and foreign has developed a cam linkage arm-grasping manipulator. This manipulator from the advantages of motor-driven, not more complex hydraulic system and its sealed buffer, no leakage, simple, reliable. Meanwhile, the manipulator arm and rotary knife inserted, the decomposition Everyone moves are linked, and some may overlap time, thus greatly reducing the time ATC。
KeyWords:Manipulator; Machining Center; Automatic tool change
设计任务
本次设计的主要任务是:自动换刀机械手,实现数控镗铣床的自动换刀,需要换的刀具主要是BT40型刀柄,需要实现的工作是抓刀—换刀—松刀的动作。
主要技术参数:刀具最大重量6kg,双臂回转式换刀,刀臂数量和长度以及直径主要依据配套刀库的设计要求。换刀时间2.5S。
机械手的平稳性
工业生产要求机械手工作速度快,运动平稳,定位精度高。应注意其影响因素,设计合理结构,以满足要求。
这篇论文主要介绍了机械手的相关资料,包括加工中心和自动换刀机械手(ATC)两部分。
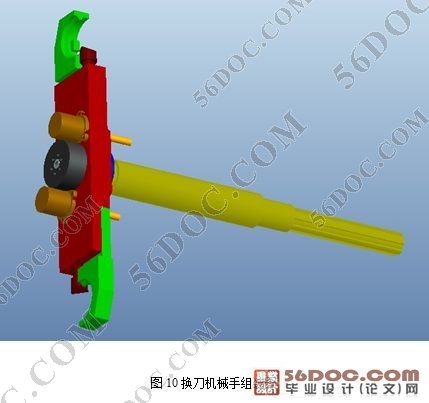
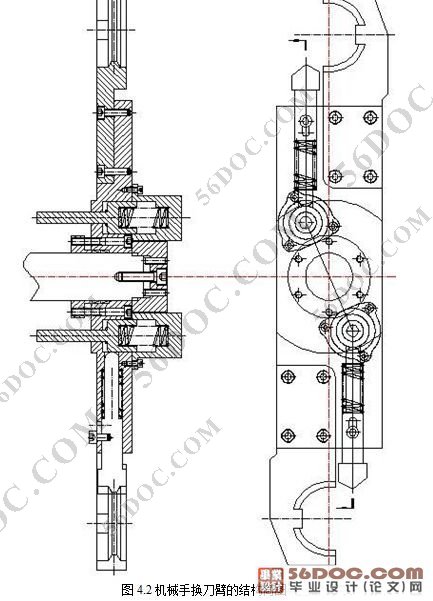
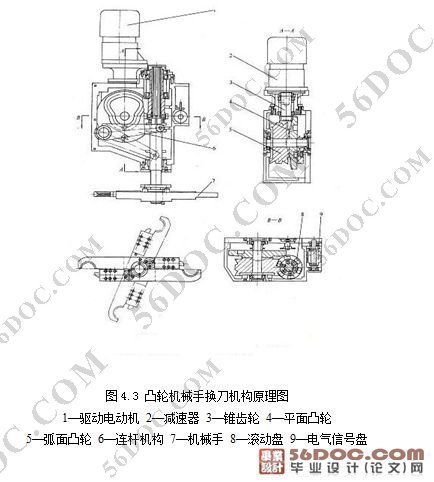
设计的主要部分是机械手的传动方式和手爪抓到的方式。传动方式的选择是通过比较3种不同类型的传动方案后确定的,这3中方案分别是气动式、液压式和凸轮联动式,通过分析,发现不论是气动式还是液压式都要求较高的加工精度,缓冲系统复杂,而且成本很高,相比而言,凸轮联动式传动不仅结构简单,工艺精度要求低,而且成本非常低廉,综上所述,选择了凸轮联动式作为我的传动方式。
凸轮联动式驱动的最大特点就是它的2个凸轮,一个是弧面凸轮,另一个是平面凸轮,其中,平面凸轮是平面凸轮和锥齿轮的合体,当电动机通过锥齿轮传动,带动平面凸轮转动时,弧面凸轮也通过键和螺栓的连接一起运动。这时,平面凸轮通过连杆,利用杠杆原理带动刀臂轴的上下移动,而弧面凸轮通过六沟珠管和刀臂轴上的花键,从而带动刀臂轴做旋转运动。
手臂的抓刀方式,是通过2个顶柱来完成的。换刀的过程是这样的,机械手先旋转80°,这时刀具和顶柱1接触,通过作用力,顶柱1回缩,刀具进入刀爪内,接下来手臂做垂直下降动作,顶柱2卡死顶柱1的位置,使顶柱1不能移动,保证了刀具在接下来的旋转中不会飞出,当手臂下降到规定位置的时候,手臂开始继续旋转180°,完成换刀,然后手臂做垂直向上运动,新刀和旧刀同时进入主轴和刀库的夹具里,这时,顶柱2回到原位,顶柱1恢复活动,最后,手臂反向旋转 80°,刀具脱离手抓,完成换刀。
这种设计的特点是结构简单,换刀时间快,成本低,非常适合推广使用。





目 录 22000字
摘 要 I
Abstract II
1 绪 论 1
1.1国内外数控机床的的发展情况 1
1.1.1 加工中心发展简史 1
1.1.2 加工中心的主要优点 2
1.1.3 加工中心的发展趋势 3
1.2可编程控制器的特点 5
2换刀机械手的相关介绍 7
2.1 数控技术的发展历程 7
2.2数控加工中心的基本功能 7
2.3加工中心的组成部分 8
2.3.1 刀库 8
2.3.2 刀具交换装置(机械手) 8
2.3.3 运刀装置 9
2.3.4 刀具编码装置 9
2.3.5刀具识别装置 10
2.4刀库的驱动及定位 10
2.5我国数控系统的发展概况 11
2.6数控系统的发展趋势 11
2.7 ATC装置的分类 11
2.8 ATC装置的换刀速度比较 13
2.9 分步双爪式ATC装置 14
2.10自动换刀系统产品化的前景 15
3 换刀机械手的总体方案设计 16
3.1 设计任务 16
3.2机械手的平稳性 16
3.2.1、影响平稳性以定位精度的因素 16
3.2.2 机械手的运动特性 17
3.3机械手运动特性的分类 18
3.4开关型机械手的速度及位置控制 18
3.5机械传动型机械手速度及位置控制 19
3.6 机械手类型确定 19
3.7 驱动系统和电控系统的选择 19
3.7.1驱动系统的选择 19
3.7.2电控系统的选择 20
4 总体结构设计 23
4.1 手爪部分设计 23
4.2 机械手手臂的设计 24
4.2.1臂部要防止偏重 24
4.2.2加强臂部刚度 25
4.2.3改进缓冲装置和提高配合精度 25
4.2.4采取的措施: 25
4.3机械手传动结构的设计 27
5 换刀机械手的参数和计算 30
5.1 手臂的弯曲变形 30
5.2 连杆的强度计算 32
5.3 驱动电动机的选择 32
6 换刀过程 35
结 论 39
参考文献 40
致 谢 42
