移动机器人AGV运动规划研究
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
移动机器人AGV运动规划研究(开题报告,论文说明书13000字,Matlab程序,CAD图1张)
摘要
随着智能技术的高速发展,路径规划越发转变为移动机器人导航的重点之一,它不单单只是找一条从起始点到终点的路径,还要综合考虑障碍物、时间等客观因素,同时优化这些因素,得到最优路径。A*算法是一种别具一格的启发式搜索算法,凭借其搜索速度快、且便捷精准受到许多学者的广泛青睐。使用其来解决路径规划问题。本文选取的算法是A*算法和贪心算法,在AGV工作环境为全局已知是静态障碍情况下,在Matlab2016a上,使用栅格法对工作环境进行建模, 其中A*算法核心是评价函数,在编写仿真程序时选取合适的启发函数将至为重要,将直接影响节点的扩展,方便减少搜索时间,进行程序仿真,在移动机器人路径规划中求得满意的路径。
关键词:机器人 路径规划 栅格法 A*算法
Abstract
With the rapid development of intelligent technologies, path planning has increasingly become one of the focuses of navigation for mobile robots. Path planning not only needs to meet the demand to make robot process from the initial point to the target point smoothly, but also considers objective factors such as obstacles and time and optimizes these at the same time. Factors, get the optimal path. A* algorithm is a kind of unique heuristic search algorithm, which is favored by many scholars because of its fast searching speed, convenient and accurate. Use it to solve path planning problems. The algorithm chosen in this paper is A* algorithm and greedy algorithm. In the case that the AGV working environment is globally known as a static obstacle, on the Matlab2016a, the grid environment is used to model the work environment, where the core of the A* algorithm is the evaluation function, Selecting the appropriate heuristic function when programming the simulation program will be very important. It will directly affect the expansion of the node, facilitate the reduction of search time, perform program simulation, and obtain a satisfactory path in the path planning of mobile robots.
Keywords: robot; path planning;grid method ;A* algorithm


目录
摘要 2
Abstract 3
第一章 绪论 6
1.1课题背景及意义 6
1.2国内外研究现状 6
1.3本课题主要研究内容 11
第二章 路径规划 13
2.1路径规划相关注意事项 13
2.2 AGV路径规划特点 13
2.3 路径规划分类 14
2.3.1全局路径规划 14
2.3.2 局部路径规划 16
2.4本章小结 18
第三章 启发式的路径规划方法 19
3.1贪心算法工作原理 19
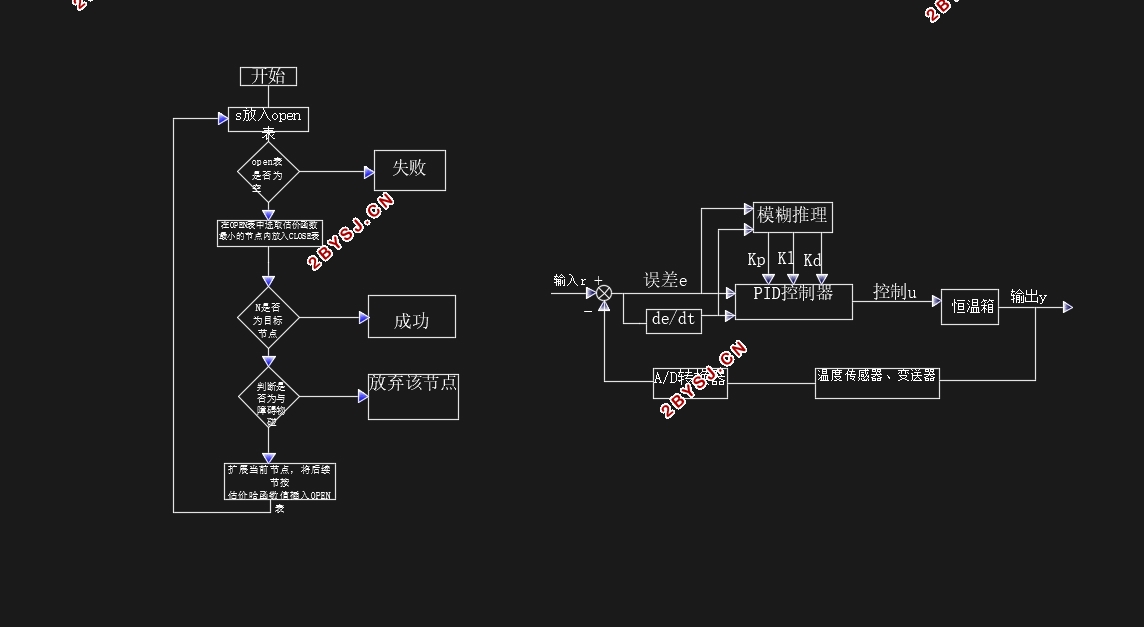
3.2 A*算法的工作原理 19
3.3 A*算法的径规划流程 20
3.4算法对比 22
3.5本章小结 22
第四章 仿真实验结果与分析 23
4.1环境模型描述 23
4.2栅格法 23
4.2.1栅格尺寸的选取 23
4.2.2栅格的标识 24
4.3A*算法基于MATLAB仿真 26
4.4贪心算法基于MATLAB仿真 28
4.5本章小结 31
总结 33
参考文献 34
致谢 36
