便携式粉尘检测仪的设计
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
便携式粉尘检测仪的设计(任务书,开题报告,论文13700字)
摘 要
近年来雾霾天气的持续出现,使得人们对于空气质量越来越重视。雾霾中主要成分为直径小于等于2.5微米的细小颗粒,又称PM2.5。PM2.5对人体危害较大,因为直径小,可以被人体吸进肺的深部,当其携带致病因子时,就会对人体造成危害。
本论文基于STC89C52单片机设计一款便携式粉尘检测器,能够实时监测空气中PM2.5的含量,使人们时刻了解空气质量,作出相应的应对措施。采用光散射法进行粉尘的检测,具有速度快、精度高的优点,是现在粉尘检测的主流方法。该系统应用3.7V锂电池供电,由升压模块升压至5V给单片机供电,采用单独模块给锂电池充电,方便简洁。
关键字:粉尘传感器;单片机;PM2.5
Abstract
In recent years, the continuous emergence of fog and haze, making people more and more attention to the quality of air. The main component of the haze is less than 2.5 microns in diameter and small particles, also known as PM2.5. PM2.5 to human body harm is bigger, because of small diameter, can be in the deep part of the human body breathe in the lung, when the carrying virulence factors will on the human body harm.
A portable dust detector based on STC89C52 microcontroller is introduced in these paper, can real-time monitoring of PM2.5 content in the air, so that people always understand the air quality, and make corresponding measures. Light scattering method is used to detect dust, which has the advantages of high speed and high precision. It is the main method of dust detection. The system uses 3.7V lithium battery power supply, by the boost module to 5V to the microcontroller to power supply, the use of a separate module to charge the lithium battery, convenient and simple.
Key words: dust sensor;single chip microcomputer; PM2.5
目 录
第1章 绪 论 1
1.1便携式粉尘检测器的概述 1
1.2粉尘检测器的国内外研究现状 1
1.3本课题选题意义和论文主要内容 2
第2章 粉尘检测器总体设计 4
2.1 理论基础 4
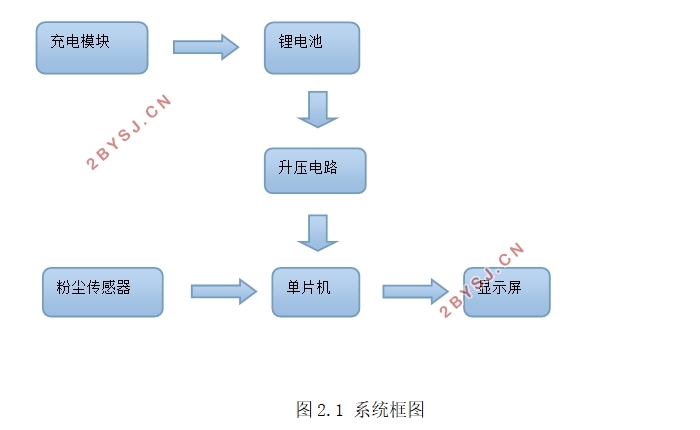
2.2 系统设计方案 4
2.3模块设计方案 5
第3章 粉尘检测器的器件选型 7
3.1主控芯片 7
3.1.1概述 7
3.1.2单片机选型 7
3.1.3 STC89C52 8
3.2粉尘传感器 9
3.2.1概述 9
3.2.2粉尘传感器的选型 9
3.2.3夏普第二代粉尘传感器 9
3.3显示模块 10
3.3.1概述 10
3.3.2显示屏的选型 11
3.3.5诺基亚5110显示模块 11
3.4升压芯片 11
3.4.1升压芯片的选型 11
3.4.2 MC34063A芯片 12
3.5锂电池充电模块 12
3.6本章小结 12
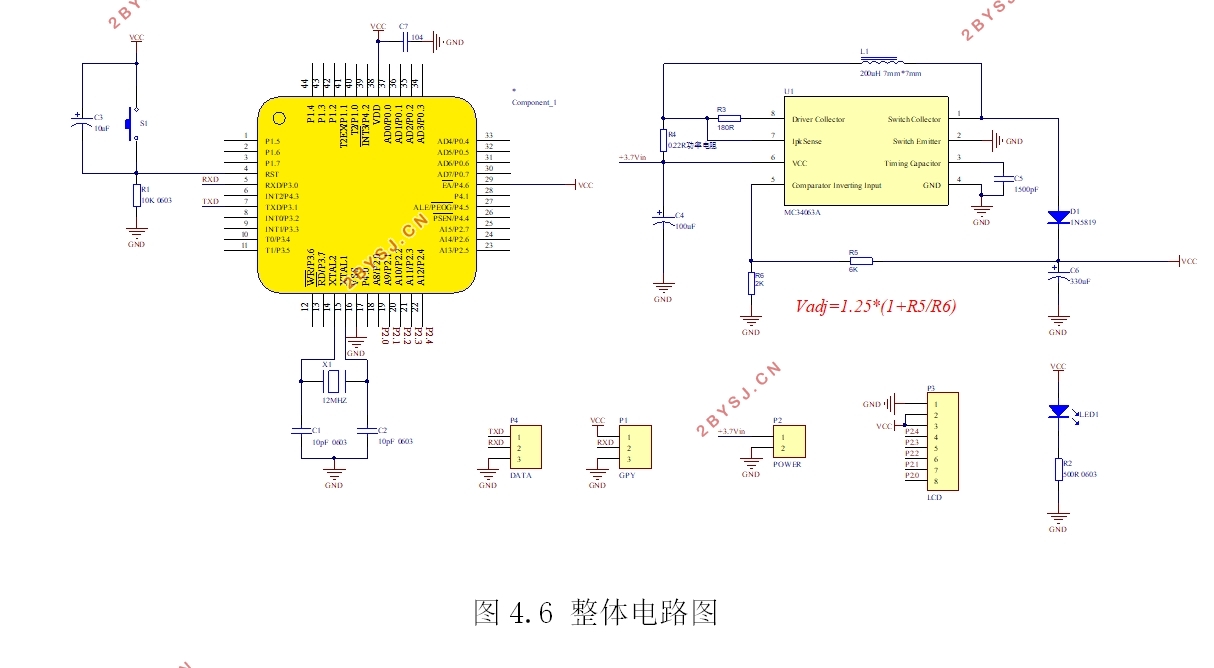
第4章 系统的搭建与测试 14
4.1 实验平台的搭建 14
4.1.1硬件部分 14
4.1.2软件部分 17
4.2粉尘检测器系统的测试 19
4.2.1硬件测试 19
4.2.2软件测试 19
4.2.3数据准确性分析 19
4.3本章小结 21
第5章 总结与展望 22
5.1总结 22
5.2展望 22
参考文献 23
致谢 25
