日处理2000吨磷矿选矿厂设计(含CAD图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
日处理2000吨磷矿选矿厂设计(含CAD图)(任务书,开题报告,论文说明书13000字,CAD图纸9张)
摘 要
选矿厂设计是矿山建设投产前极其重要的关键部分,它直接为项目的决策提供科学依据。当项目决定以后,它又是项目执行的指导文件。另外,它也是科学技术转化为生产力的媒介,生产中的先进技术、科研成果及先进经验,都需要用设计来推向生产实践。选矿厂设计的要求也随着矿物加工技术的发展逐步提高。
本次设计原矿来自湖北大峪口胶磷矿,计划产量为2000t/d。该原矿作为我国低品位磷矿的代表,其单体解离困难,共生关系复杂,为浮选设计带来巨大困难。设计沿用双反浮试验流程,最终可将磷矿品位由16.47%提升至28.35%,同时回收率达到82.30%。在此基础上根据矿石性质确定其他工艺流程以及工艺设备的选择:破碎采用三段一闭路流程,磨矿采用两段全闭路流程,精矿采用先浓缩后过滤的两段脱水。同时综合当地地区地理和交通情况,对选矿厂的选址与建设进行设计。
关键字:选矿厂设计 ;胶磷矿;双反浮选;2000吨/天
Abstract
The design of the concentrator is extremely important part of the mine construction, which directly provide a scientific basis for decision-making project. When the projece is decided, it is the guiding document for project implementation. In addition, it is also a science and technology into productive forces of the media. Production of advanced technology, research and best practices, are necessery to push the design production practice.With the continuous development of the mineral processing industry,concentrator design requirements are also rising.
The design of the ore from Hubei Dayukou collophane planned production of 2000t/d. The low-grade ore as the representative of our phosphate rock, which monomer dissociation difficult, causing great difficulties for flotation design. Dual float design follows the testing procedures, the final grade phosphate rock can be increased from 16.47 to 28.35 percent, while the recovery rate of 82.30%. On this basis, determine the selection process and other process equipment in accordance with the nature of the ore: a closed-circuit crushing three-stage process, the full closed-circuit grinding two-stage process, using the concentrate after the first two paragraphs concentrate filtration dehydration. Siting and construction of the concentrator design should combine the local geography and traffic conditions.
Key Words: concentrator desig;collophanite ore;double-reverse floation;the capacity of 2000t/d
2.1 选矿厂的规模及服务年限
(1)规模:日处理2000吨;
(2)选定指标:①磨矿细度为:-0.074mm占94.23%
②原矿最大粒度Dmax=500mm
2.2 选矿厂工作制度与设备作业率
设计该选矿厂工作制度与各车间设备作业率见表2.1。
表2.1 选矿厂工作制度与各车间设备作业率
车间名称 工作制度 年运转
小时数 设备作
业率/%
性质 日/年 班/日 时/班
破碎 间断 300 2 7 4200 47.95
磨浮 连续 300 3 8 7200 82.19
脱水干燥 连续 300 3 8 7200 82.19
尾水处理 连续 300 3 8 7200 82.19


目录
第1章 绪论 6
1.1目的及意义(含国内外的研究现状分析) 6
1.1.1研究目的 6
1.1.2研究意义 6
1.1.3国内外研究现状分析 7
1.1.4胶磷矿简介 7
1.2基本内容和技术方案 8
1.2.1基本内容 8
1.2.2技术方案 9
第2章 选矿厂的规模与工作制度 10
2.1 选矿厂的规模及服务年限 10
2.2 选矿厂工作制度与设备作业率 10
2.3 选矿厂小时处理矿量 10
第3章 选矿工艺流程的选择与计算 11
3.1 破碎筛分流程的选择与计算 11
3.2磨矿分级的计算 13
3.3浮选流程的计算 17
3.4矿浆流程的计算 22
第4章 主要工艺设备的选择与计算 31
4.1 破碎筛分车间设备的选择与计算 31
4.1.1 Ⅰ段粗碎设备的选择与计算 31
4.1.2 Ⅱ段中碎破碎机的选择与计算 32
4.1.3 III段细碎破碎机的选择与计算 33
4.2 筛分设备的选择与计算 33
4.3磨浮车间设备的选择与计算 35
4.3.1 磨矿设备 35
4.3.2分级设备 37
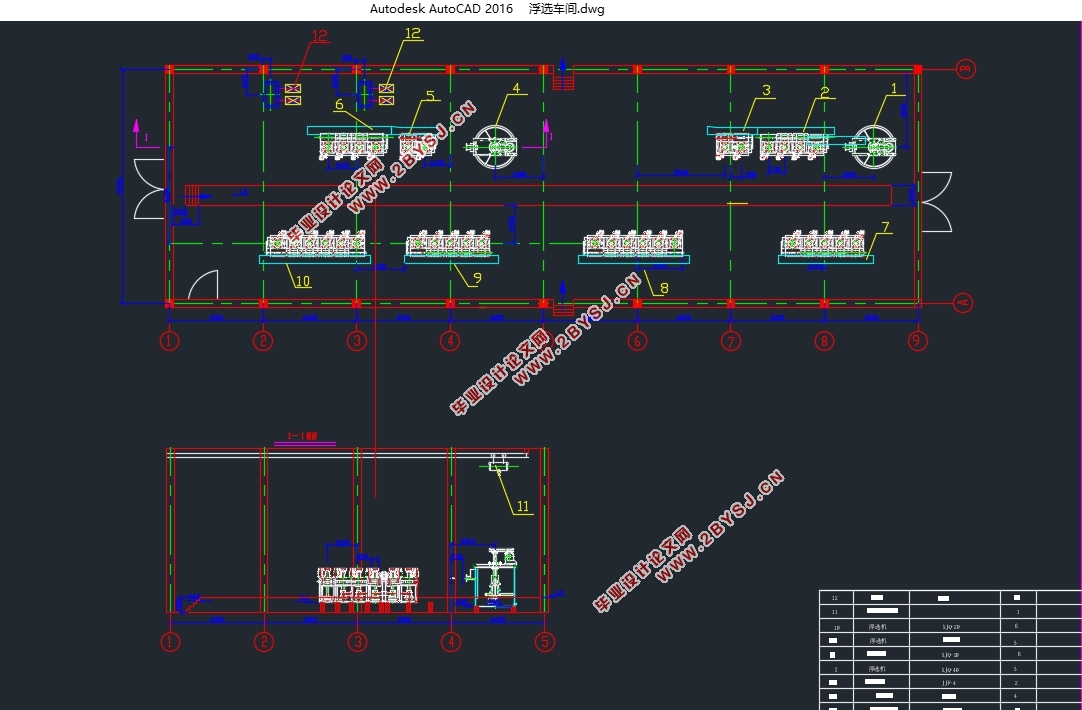
4.3.3 浮选设备 39
4.4脱水设备的选择与计算 44
4.4.1 浓缩机的计算 44
4.4.2 过滤机的计算 46
4.4.3 干燥机的计算 46
第5章 辅助设备的选择与计算 48
5.1 矿仓 48
5.2 给料机 49
5.2.1粗碎机给料机 49
5.2.2磨矿机给料机 50
5.3 皮带运输机的选型和计算 50
5.3.1皮带宽度的计算 50
5.3.2按最大块度校核 50
5.3.3传动滚筒功率 51
5.3.4计算电动机功率 51
5.4 储矿浆搅拌槽的选择计算 51
5.5 泵的选择计算 52
5.5.1 尾矿输送泵(1#、2#泵)的选择与计算 52
第6章 结论 54
参考文献 55
附录 56
致谢 57
