不同类型石油磺酸钠浮选萤石试验研究
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
不同类型石油磺酸钠浮选萤石试验研究(任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文15000字)
摘 要
萤石是重要的非金属矿产资源,是制备氢氟酸的主要原料,在氟工业上有着重要用途。随着工业化的开采和使用,导致萤石矿逐渐贫化,品位较低,并且萤石矿多与方解石、石英、重晶石等矿物伴生,工业上通常需要经过多次精选和扫选来提高萤石精矿的品位。广泛使用的萤石捕收剂是油酸钠,而油酸钠的不耐低温等特点导致特殊工况下浮选效果显著变差,因此探索高效耐低温萤石浮选捕收剂的研究意义重大。
本文以萤石纯矿物为实验对象,通过纯矿物浮选试验探究了在不同温度条件下萤石在不同种类型石油磺酸钠体系下的浮选行为,以及不同类型石油磺酸钠捕收性能的差异,同时与常规捕收剂油酸钠对萤石的捕收行为进行对照研究,并通过Zeta电位测试、傅里叶红外光谱分析(FTIR)以及接触角测试(CA)等手段分析探究了浮选药剂与矿物的作用机理,主要结论如下:
(1)石油磺酸钠在浓度为3.33×10-3mol/L时对萤石有较好的捕收效果,石油磺酸钠中活性物含量越高,达到最佳浮选效果的用量越低。对于分子量相同的石油磺酸钠,在浓度用量一致时,活性物含量越高,石油磺酸钠作用能力越低;芳烃含量越高,石油磺酸钠对萤石的捕收效果也更差。
(2)添加一定量的正丁醇有助于HL-FXJ-J3-1石油磺酸钠在矿浆中的溶解,但加入量大于药剂质量的3%以上后促进溶解作用趋于稳定。
(3)除含石蜡基药剂HL-FXJ-J3-1外,石油磺酸钠的耐低温性普遍良好,在常温回收率相近的情况下,低温浮选的回收率明显高于油酸钠,且分子量越大的药剂对温度的敏感度越低。
(4)要在常温下达到同样的浮选指标,石油磺酸钠的药剂浓度远大于油酸钠。
(5)机理分析测试结果表明,油酸钠作用后萤石表面电位平均下降水平较石油磺酸钠药剂低,可认为油酸钠在萤石表面的吸附量低导致其低温捕收性能不如石油磺酸钠。药剂对萤石的捕收性能差,原因在于萤石表面的药剂吸附量过小,未改变其表面亲水性。吸附量过大可能对萤石浮选产生抑制作用,但对低温的抵抗性强。
关键词:萤石;纯矿物;低温;石油磺酸钠;油酸钠
Abstract
Fluorite is an important non-metallic mineral resource, whichplays an important role in the fluorine industry as the main raw material for hydrofluoric acid production. Through industrial exploitation, fluorite ore is gradually depleted leading a lowergrade, and the fluorite ore usually has a paragenesis relations with calcite, quartz and barite. It requires several times of scavenging and cleaning to improve the grade of fluorite concentrate in the industry. The widely used collector of fluorite is sodium oleate, whose characteristics such as no anti-low temperaturewould lead to a significant deterioration of the flotation effect under special industry conditions. Therefore, it is meaningful to find an effective low-temperaturefluorite flotation collectors.
This paper usespure fluorite mineralsas the experimental subject to explore the collection performance and differences to concentrate fluorite in various types of petroleum sulphonate under different temperature conditions,which is also compared with the conventional collector sodium oleate. And analysing the mechanism of action of agents and mineralsthrough the Zeta potentialanalysis, Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy(FTIR) and contact angle tests(CA). The main contentsinclude following aspects:
1. The sodium petroleum sulfonates have a good effect on the collection of fluorite when the amount is 3.33×10-3mol/L. The larger the content of active substance, the less the amount can be used to achievetheflotation effect.For agents with the same molecular weight, the agent with a higher active content has a poor ability to actwhen the consumption is the same; the higher the content of aromatics, the less the adsorption effect of the agent on fluorite.
2. The addition of a certain amount of n-butanol contributes to the dissolution of the HL-FXJ-J3-1 agent in the slurry, but tends to be stable when the amount added is greater than 3% of the mass of the agent.
3. In addition to the paraffin-based agent HL-FXJ-J3-1, the sodiumpetroleum sulfonate has good quality of low-temperature resistance, and recovery at low temperature flotation is significantly higher than that of sodium oleate whileit is similar at room temperature. The odiumpetroleum sulfonate with larger the molecular weight is less sensitive to temperature.
4. To achieve the same flotation index at room temperature, the amount of sodium sulfonate is much greater than that of sodium oleate.
5. The results of the mechanistic analysis and test showed that the average decrease in the surface potential of fluorite after sodium oleate treatment was lower than that of being treated by petroleum sodiumsulfonate. It was considered that the low adsorptive capacity of sodium oleate on the surface of fluorite resulted in inferiorlow temperature collection performance.The poorcollection performance of the agent was because the adsorbed amount on the fluorite surface was too small to change the surface hydrophilicity. Excessive adsorption may inhibit fluorite flotation but resist low temperatures.
Key Words:Fluorite;pure minerals;low temperature;petroleum sulfonate;sodium oleate
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 萤石资源概况 1
1.2 萤石浮选捕收剂研究现状 1
1.2.1 常温捕收剂 2
1.2.2 低温捕收剂 3
1.2.3 不同类型捕收剂作用机理 4
1.3 研究目的及意义 5
第2章 试验原料、试剂及试验研究方法 6
2.1 试验原料 6
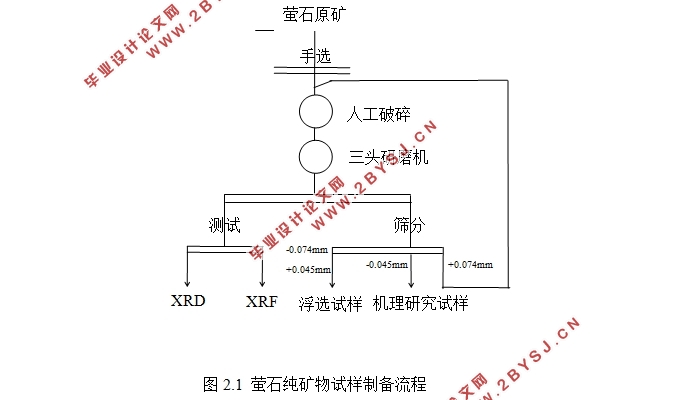
2.1.1 实验试样制备 6
2.1.2 试样分析 6
2.2 实验药剂及设备 7
2.2.1 实验试剂 7
2.2.2 实验设备及仪器 8
2.3 实验方法 9
2.3.1 纯矿物实验 9
2.3.2 Zeta电位测定 10
2.3.3 红外光谱测试 10
2.3.4 接触角测试 11
2.3.5 X射线衍射分析 11
第3章 纯矿物浮选结果与讨论 12
3.1 石油磺酸钠浓度实验 12
3.2 pH值条件实验 13
3.3 不同类型石油磺酸钠常温浮选实验 13
3.3.1 活性物含量对药剂浮选性能的影响 15
3.3.2 芳烃含量对药剂捕收性能的影响 16
3.3.3 添加正丁醇对药剂捕收性能的影响 16
3.4 不同类型石油磺酸钠低温浮选实验 17
3.5 油酸钠浮选实验 20
3.5.1 油酸钠浓度实验 20
3.5.2 油酸钠常温与低温浮选实验 21
3.6 小结 23
第4章 机理分析 24
4.1 Zeta电位测试结果 24
4.2 药剂与矿物作用红外光谱分析 26
4.3 接触角测试结果 28
第5章 结论 32
参考文献 33
致 谢 35
