主动径向转向架概念设计及轮对磨耗机理分析(含CAD图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
主动径向转向架概念设计及轮对磨耗机理分析(含CAD图)(任务书,开题报告,文献摘要,外文翻译,论文说明书29000字,CAD图3张)
摘要
轨道车辆在行驶的过程中,轮对与轨道之间会发生一定的相对滑动,尤其是在曲线行驶中显得尤为明显,这种现象被称为轮对的蠕滑现象。随着科技技术的不断发展,现代的轨道车辆无论是干线铁路还是地铁线路其运行速度都在不断地提升,负载重量也得到了提高,此外,现代的高速轨道车辆为了获得一定的稳定性,通常会伴随着较差的弯道通过性能,这一系列的问题都会造成轮对与轨道之间的蠕滑力过大。当蠕滑力过大时会导致轮对磨耗过度,缩短转向架的使用寿命,造成大量的能量浪费与环境污染的同时还会增加铁路运输成本,影响铁路的正常运输。
本论文设计了一种能够主动径向转向的转向架,通过主动控制转向架的前后轮对偏转实现主动径向转向,以此来改善列车曲线通过性能,降低轮对的磨耗,提高车辆过弯安全性。本文通过SOLIDWORKS建模软件对转向架整体进行建模,采用SIMPACK内置控制单元对主动径向转向架的动力学性能进行建模仿真研究,并分析了轮对磨耗发生机理,将主动径向转向架同传统转向架的磨耗进行对比研究。具体的研究工作如下:
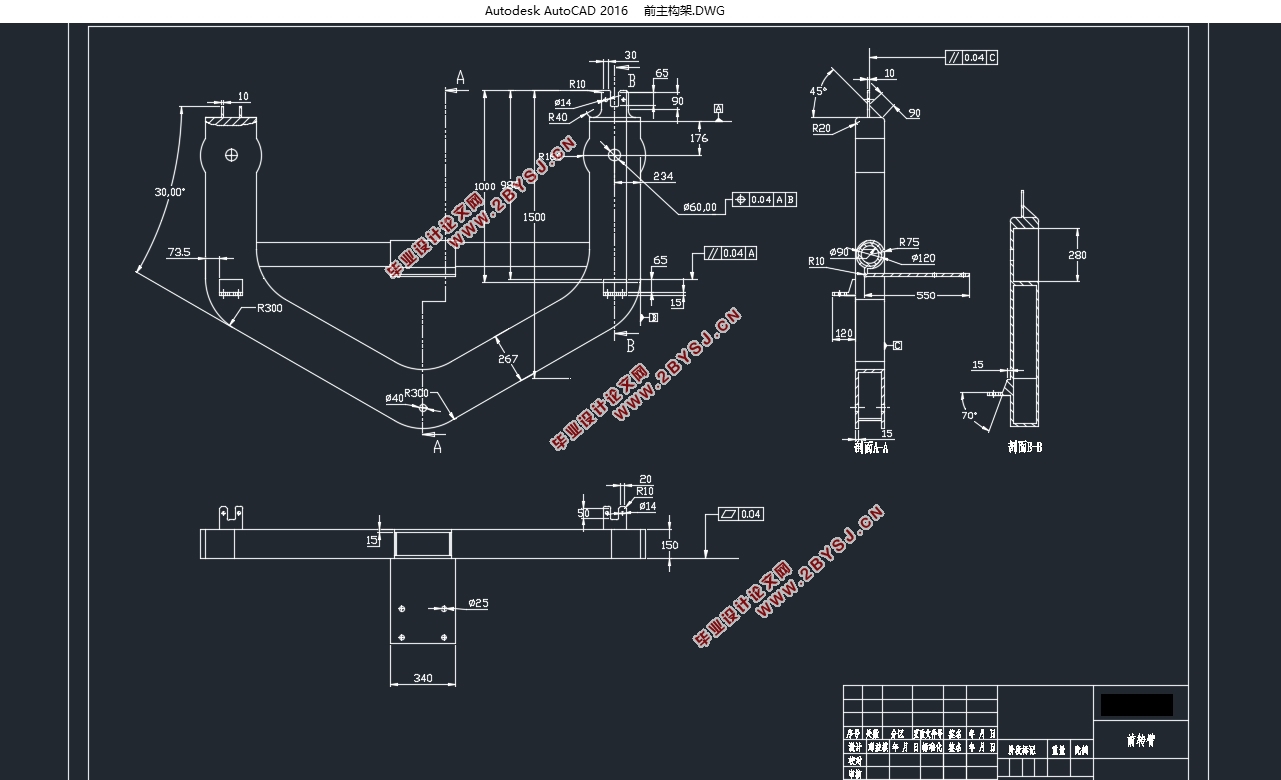
1、主动径向转向架概念设计。首先对主动径向转向机理进行了分析,随后介绍了转向架SOLIDWORKS模型的构成及各部分的作用,主要包括有主副构架结构、一系悬挂装置、二系悬挂装置以及一些其他的附加装置。
2、主动径向转向架的动力学模型建立。建立了主动径向转向架列车与传统转向架列车的SIMPACK整车仿真模型,为后续章节奠定基础。
3、主动径向转向架动力学性能分析。对装配了主动径向转向架的列车进行了直线运行稳定性仿真,仿真结果表明列车的直线运行速度达到290km/h列车才会出现蛇形运动,能满足实际工程需求。对列车的直线运行平稳性进行了仿真,结果表明横向及垂向平稳性均处于“好”—“可以运行”之间,平稳性能良好。同时还仿真分析了列车的曲线通过性能,结果表明当列车的过弯速度≤70km/h时,内外轨的脱轨系数均小于0.6,达到了优秀评级。
4、主动径向转向架与传统转向架轮轨磨耗对比分析。首先对列车的磨耗机理进行了介绍,并选取了相应的滚动接触理论以及磨耗评价指数。随后仿真分析了三种速度下的主动径向转向架列车与传统转向架列车的磨耗指数WearNumber,结果表明无论在什么速度下,主动径向转向架的过弯磨耗量均要比传统转向架小很多。最后将三种速度下的主动径向转向架冲击轮对车轮进行对比,结果表明70km/h时是主动转向架的最佳过弯速度,这时其车轮综合磨耗最小。
关键词:主动径向转向;传统转向架;SIMAPCK仿真;磨耗对比分析
Abstract
In the running process of rail vehicles, relative slip will occur between wheelset and track, especially in curvilinear running. This phenomenon is known as the creep phenomenon of wheelset. With the continuous development of science and technology,the running speed of the modern railway vehicles trunk railway lines and subway lines is in constant increase, the load weight is improved, moreover, the modern high-speed railway vehicles in order to obtain a certain stability, often accompanied by poor performance through corners through the, this series of problems will cause excessive creep force between wheel and track. When the creep force is too large, it will cause excessive abrasion of wheelset, shorten the service life of bogie, cause a lot of energy waste and environmental pollution, and at the same time increase the cost of railway transportation and affect the normal railway transportation.
This paper designs a kind of bogie capable of active radial steering, which can achieve active radial steering by actively controlling the deflection of the front and rear wheelsets of the bogie, so as to improve the passing performance of train curves, reduce the wear of wheelsets and improve the safety of vehicle bending. In this paper, the whole bogie is modeled with SOLIDWORKS modeling software, and the dynamic performance of the active radial bogie is modeled and simulated with the built-in control unit of SIMPACK, the mechanism of wheel set abrasion is analyzed, and the abrasion of the active radial bogie is compared with the traditional bogie. Specific research work is as follows:
1. Concept design of active radial bogie. Firstly, the mechanism of active radial steering is analyzed, and then the SOLIDWORKS model of bogie and the functions of each part are introduced.
2. Establishment of dynamic model of active radial bogie. The SIMPACK vehicle simulation model of active radial bogie train and traditional bogie train is established, which lays a foundation for the following chapters.
3. Dynamic performance analysis of active radial bogie. The linear running stability simulation of the train equipped with active radial bogie is carried out, and the simulation results show that only when the maximum linear running speed of the train reaches 290km/h will the train have snaking movement, which can meet the actual engineering requirements. The simulation results show that the horizontal and vertical stationarity are between "good" and "runnable", and the stationarity is good. At the same time, the curve passing performance of the train is simulated and analyzed. The results show that when the bending speed of the train is less than 70km/h, the derailment coefficient of the inner and outer rails is less than 0.6, reaching the excellent rating.
4. Comparative analysis of wheel and rail abrasion between active radial bogie and traditional bogie. Firstly, the wear mechanism of the train is introduced, and the rolling contact theory and wear evaluation index are selected. Then, the Wear index Wear Number of the active radial bogie train and the traditional bogie train under the three speeds was simulated and analyzed. The results showed that the bending Wear of the active radial bogie was much smaller than that of the traditional bogie at any speed. Finally, a comparison is made among the wheels of the active radial bogie at three speeds. The results show that the best bending speed of the active bogie is 70km/h, and the comprehensive wear of each wheel is the minimum.
Keywords: active radial steering; Traditional bogie; SIMAPCK simulation; Comparative analysis of abrasion
本文主要研究工作
本文主要的研究对象为主动径向转向架,论文内容主要包括有主动径向转向架的概念设计、主动径向转向架动力学性能分析、磨耗理论研究以及传统转向架与主动径向转向架磨耗对比分析。
研究内容总体安排如下:
1、主动径向转向架概念设计。对主动径向转向架的径向原理进行分析。介绍转向架模型的构成及各部分的功能,主要包括有主副构架结构、一系二系悬挂装置以及电机驱动装置等;
2、主动径向转向架动力学模型的建立。介绍动力学仿真研究内容及理论依据,建立主动径向转向架与传统转向架的整车仿真模型,为后续章节奠定基础;
3、分析主动径向转向架的动力学性能,主要包括有直线稳定性、直线平稳性以及曲线通过性;
4、主动径向转向架以及传统转向架磨耗对比分析。讨论现有的转向架轮对磨耗机理,选取合适的磨耗理论以及磨耗评价标准,对比分析轮对磨耗情况;
5、结论。对整个主动径向转向架的概念设计、动力学性能分析、轮对磨耗机理研究以及磨耗对比分析进行梳理与总结,讨论本文研究的创新性以及局限性,并提出对主动径向转向架技术后续研究的主要展望。


目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景与意义 1
1.2 国内外径向转向架的发展过程 2
1.2.1径向转向架的概念 2
1.2.2国内外径向转向架的发展 3
1.3国内外研究现状 5
1.3.1径向转向架 5
1.3.2轮对磨耗 6
1.4本文主要研究工作 7
第2章 主动径向转向架模型设计 8
2.1主动径向转向架原理 8
2.2径向转向架整体布局设计 8
2.3主动径向转向架主要构件 9
2.3.1主构架 9
2.3.2副构架 10
2.3.3一系悬挂装置 11
2.3.4二系悬挂装置 12
2.3.5其他装置 14
2.4传统转向架与主动径向转向架对比 16
2.5本章小结 17
第3章 基于SIMAPACK的整车动力学仿真模型构建 18
3.1车辆动力学研究内容 18
3.1.1车辆运行稳定性 18
3.1.2车辆运行平稳性 19
3.1.3车辆曲线通过性 20
3.2仿真软件介绍 21
3.3整车仿真模型 21
3.4 本章小结 25
第4章 转向架动力学性能分析 26
4.1运行稳定性 26
4.2运行平稳性 27
4.3曲线通过性能 30
4.4本章小结 33
第5章 磨耗分析 34
5.1 磨耗机理 34
5.2 传统转向架与主动径向转向架磨耗对比 36
5.3主动径向转向架最佳过弯速度 38
5.4本章小结 40
第6章 结论 41
6.1 研究总结 41
6.2 研究展望 42
参考文献 43
致 谢 45
