抽汽凝汽式汽轮机主汽阀结构及加工工艺设计(含CAD图,SolidWorks三维图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
抽汽凝汽式汽轮机主汽阀结构及加工工艺设计(含CAD图,SolidWorks三维图)(任务书,开题报告,论文说明书17000字,CAD图10张,SolidWorks三维图)
摘要
主汽阀是控制汽轮机高压蒸汽通断的总阀门,安装在进汽口,是汽轮机的主要辅机之一。近年来随着汽轮机功率及额定蒸汽压力的增大,高压主汽阀的使用逐渐普及,高压主汽阀的设计及加工成为汽轮机辅机研究的热点。高压主汽阀高温高压的工作条件决定了其结构强度及零件加工精度都有较高的要求。
本文针对C25-8.83/0.98抽汽凝汽式汽轮机的主汽阀,研究其结构设计及加工工艺设计。针对主汽阀的结构设计,首先进行总体设计,确定主汽阀的布置方式、密封方式及操纵系统等;然后进行主汽阀关键零部件的结构设计,绘制零件图及整体装配图,完成设计过程。结构设计使用SolidWorks建立了主汽阀零部件及装配体的三维模型,使用ANSYS软件进行有限元分析,校核在工作条件下设计零件是否满足使用要求。加工工艺设计的主要方法是基于零件图纸和三维模型提取零件的主要结构特征及加工要求,确定零件的主要加工方法及加工工艺,选择加工设备,确定生产过程中的各加工工艺,制成零件的加工工艺过程卡片和工序卡片,完成零件的加工工艺设计。
关键词:汽轮机、主汽阀、结构设计、有限元分析、工艺设计
Abstract
The main steam valve is the main valve that controls the on-off of steam turbine high-pressure steam. It is installed in the steam inlet and is one of the main auxiliary machines of the steam turbine. In recent years, with the increase of steam turbine power and rated steam pressure, the use of high-pressure main steam valves has become increasingly popular. The design and processing of high-pressure main steam valves has become a hot topic in turbine auxiliary engines. High pressure main steam valve work under high temperature and high pressure determines its structural strength and parts processing accuracy have higher requirements.
This paper aims at the main steam valve of C25-8.83/0.98 steam extraction condensing steam turbine, and studies its structural design and processing technology design. For the structural design of the main steam valve, first overall design, determine the layout of the main steam valve, sealing method and control system, etc.; then the main steam valve key components of the structural design, drawing parts and overall assembly drawings, complete design process. Structural Design SolidWorks was used to establish a three-dimensional model of the main steam valve components and assemblies. ANSYS software was used to perform finite element analysis to check whether the design parts meet the requirements for use under working conditions. The main method of process design is to extract the main structural features and processing requirements of the parts based on the parts drawings and 3D models, determine the main processing methods and processing technology of the parts, select the processing equipment, determine the various processing technologies in the production process, and make the parts Process card process card, complete the processing technology design of parts.
Keywords: steam turbine, main steam valve, structural design, finite element analysis, process design
本文主要研究内容及研究路线
本论文的目标是设计C25-8.83/0.98抽汽凝汽式汽轮机的主汽阀,对该型号主汽阀的主要零部件进行结构设计;对关键零部件进行有限元分析并设计关键零部件的加工路线。C25-8.83/0.98抽汽凝汽式汽轮机的额定功率25MW,新蒸汽压力8.83MPa,调节抽汽压力0.98MPa,属于高压汽轮机。通过本次设计,获得满足高压汽轮机使用要求的主汽阀主要零部件的结构及加工工艺流程。
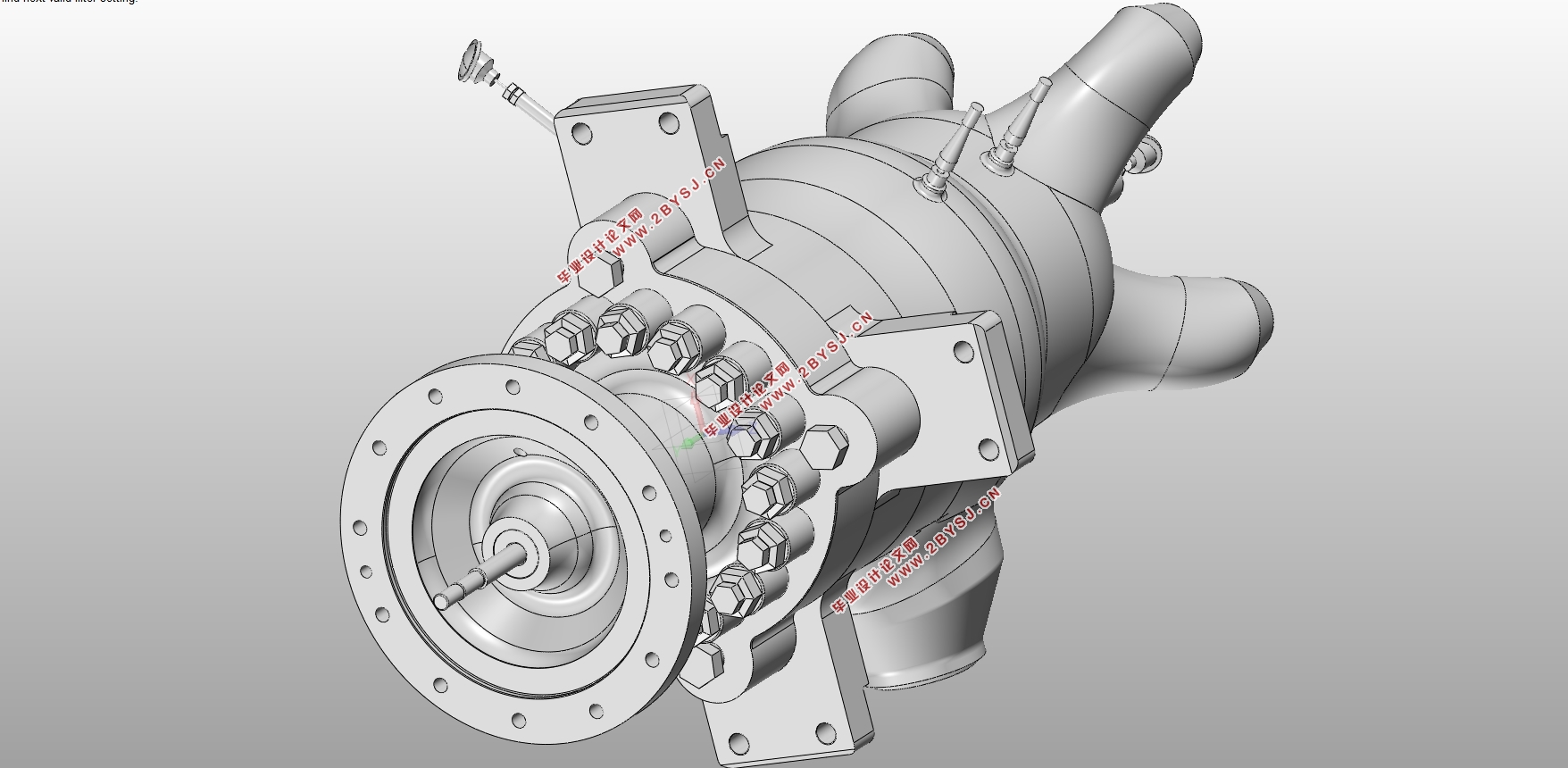
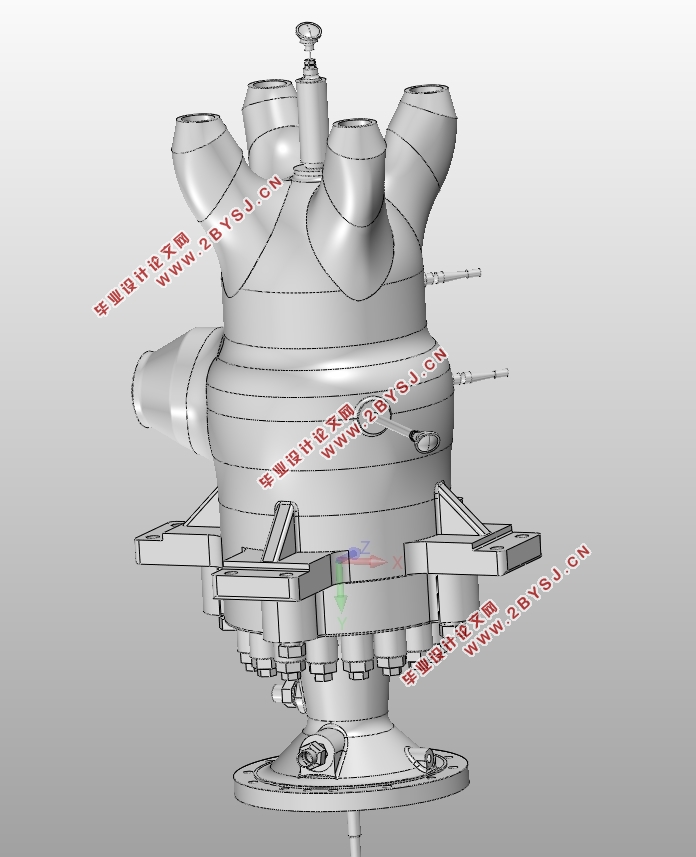
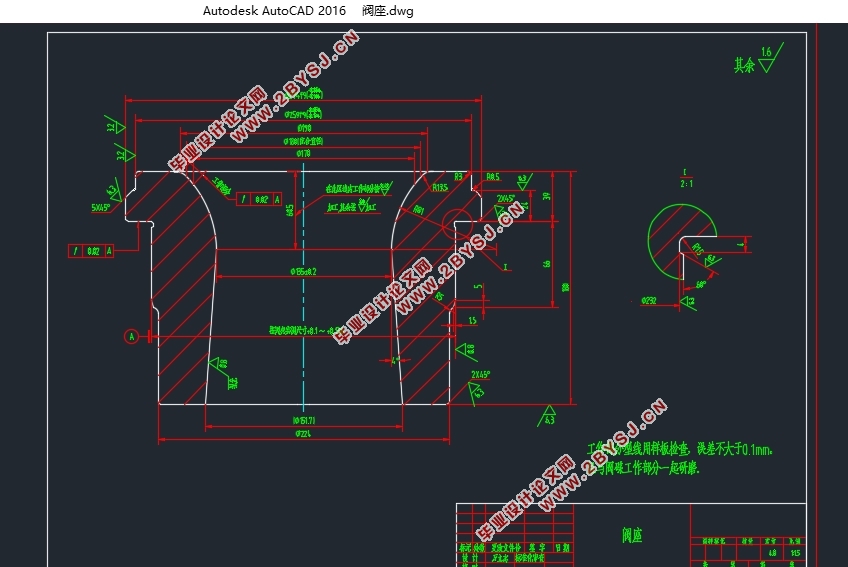
在主汽阀结构设计方面,主汽阀包含零件较多,其中主要零件有阀壳、阀盖、阀碟、阀碟套筒、阀座、阀杆、阀杆套筒等。在进行零部件的结构的设计时,先根据C25-8.83/0.98汽轮机主汽阀的使用要求、工作环境等条件,结合热力学计算和机械结构强度计算,获得零件主要参数,再进行工厂实地调研,参考正在生产的其他型号高压主汽阀对应零件的结构,完成零件的结构设计并绘制零件的二维工程图。结构设计完成后,建立零件的三维模型并进行有限元分析,通过仿真确定零件在工作过程中的应力分布、极限应力大小以及危险截面的位置,并校核设计结果是否满足使用要求。
在零件的加工工艺方面,加工工艺设计的主要技术方案是基于三维零件模型的工艺路线设计[7]。对单个零件,先从三维模型中提取零件的加工特征,以加工特征为根据确定零件的主要加工方法,再将多种加工方法进行排序并细化获得零件的加工路线。之后进入工厂产线进行调研,将设计的加工工艺路线与其他型号的主汽阀加工路线比较并根据产线情况进行适当修改,做出各零件的加工工艺卡片,完成整个加工工艺的设计。




目录
摘要 II
Abstract III
第一章绪论 1
1.1选题背景 1
1.2国内外研究现状综述 1
1.3本文主要研究内容及研究路线 2
第二章主汽阀结构设计 3
2.1引言 3
2.2主汽阀整体结构设计 3
2.2.1布置方式的选择 3
2.2.2 主汽阀操纵机构的选择 3
2.2.3 主汽阀密封方式的选择 4
2.3阀壳的结构设计 5
2.3.1阀壳进汽管口径的设计 5
2.3.2阀壳壁厚的设计及校核 6
2.4主汽阀阀盖的设计 8
2.5主汽阀阀杆的设计 9
2.6本章小结 12
第三章主汽阀零部件的有限元分析 13
3.1引言 13
3.2阀壳的水压试验的有限元分析 13
3.2.1 阀壳水压试验工况 13
3.2.2阀壳有限元模型的建立 13
3.2.3阀壳水压试验的有限元分析 14
3.3阀壳工作条件下的有限元分析 17
3.3.1 工况下阀壳有限元模型的建立 17
3.3.2施加载荷及建立约束 17
3.3.3有限元分析网格的划分 19
3.3.4有限元分析结果 19
3.4本章小结 20
第四章主汽阀加工工艺 21
4.1 引言 21
4.2阀杆的加工工艺 21
4.2.1 阀杆材料分析 21
4.2.2 阀杆零件图样分析 21
4.2.3 阀杆加工工艺的设计 22
4.2.4阀杆的热处理工艺 23
4.2.5阀杆加工时刀具及切削参数 24
4.2.6阀杆的加工工艺过程卡 26
4.3阀壳的加工工艺 27
4.3.1 阀壳的材料性质 27
4.3.2阀壳零件图样分析 27
4.3.3阀壳加工工艺的设计 28
4.3.4阀壳的热处理工艺 29
4.3.5阀壳的加工工艺过程卡 29
4.4阀杆套筒的加工工艺 31
4.4.1阀杆套筒材料分析 31
4.4.2阀杆套筒零件图样分析 31
4.4.3阀杆套筒加工工艺设计 32
4.4.4阀杆套筒的热处理工艺 32
4.4.5 阀杆套筒的加工工序卡片 33
4.5 本章小结 33
第五章结论 34
5.1 全文总结 34
5.2 研究展望 34
致谢 35
参考文献 36
