轮式移动机器人的结构设计(含cad零件图和装配图)
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
轮式移动机器人的结构设计(含cad零件图和装配图)(含任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文说明书18000字,CAD图纸4张)
摘要:本文首先对机器人的国内为发展现状做了介绍,同时根据设计要求对机器人的整体方案进行了分析,包括几何尺寸、控制芯片的选择。然后从机器人性能要求的角度出发,分别对机器人的运动方式、模型结构和车体成型方式做了比较,最终确定了非完整约束轮驱四轮式移动结构模型——后轮同轴驱动,前轮转向的轮型机器人。
本文对移动机器人硬件结构做了详细的可行性分析及设计,并且做了相应的计算、校核,主要包括:驱动轮电机和转向轮电机的选择;齿轮的设计计算和校核;前后减震系统以及转向机构设计和车体的一些机械结构设计等。对轮式移动机器人的运动学特性进行了分析,建立了不考虑滑行、刹车等的轮式移动机器人的运动学模型。
最后,本文对所作研究和主要工作进行了总结,并将设计的轮式机器人的结构进行联合调试。实验结果表明,该系统性能稳定、可靠,可控制性高,安全性高,达到了本设计的设计要求。
关键字:轮式移动机器人 运动学模型 结构设计
The structural design of the wheeled mobile robot
Abstract: First in the paper for the domestic present situation of the development of the robot is presented, and according to the design requirements of the overall plan for robots are analyzed, including geometry size and control chip choice. Then from the Angle of robot performance requirements respectively, the robot mode of motion, model structure and body forming method are compared, final nonholonomic constraint four wheel drive wheeled mobile structure model, rear wheel drive coaxial, front wheel steering wheel robot.
In this paper, the mobile robot hardware structure of a detailed feasibility analysis and design, and make the corresponding calculation, checking, mainly including: the drive wheels motor and motor turning wheels choice; The design of gear calculate and check; Before and after the damping system and steering mechanism design and some of the mechanical structure design of the body. Wheeled mobile robots to the kinematic characteristics, the paper builds don't consider taxi, brake of the robot kinematics model.
Finally, this paper study and main work are summarized, and the wheel will design the structure of the robot joint debugging. The experimental results show that the system has stable performance, reliable, but controlling high, high safety, achieve the design design requirements.
Keywords: wheeled mobile robots kinematics model structure design
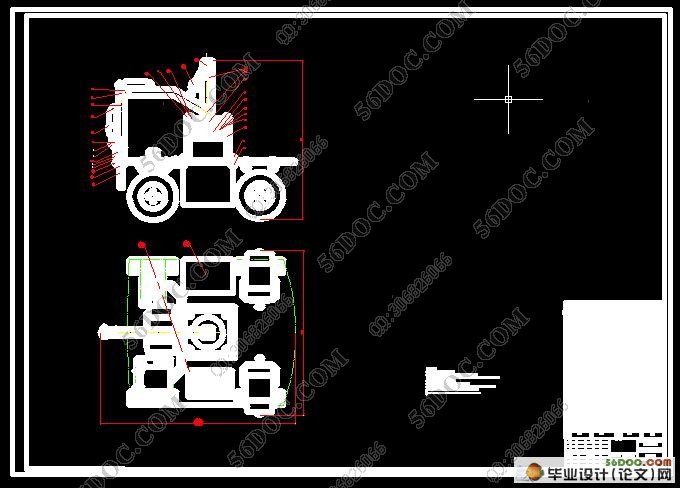
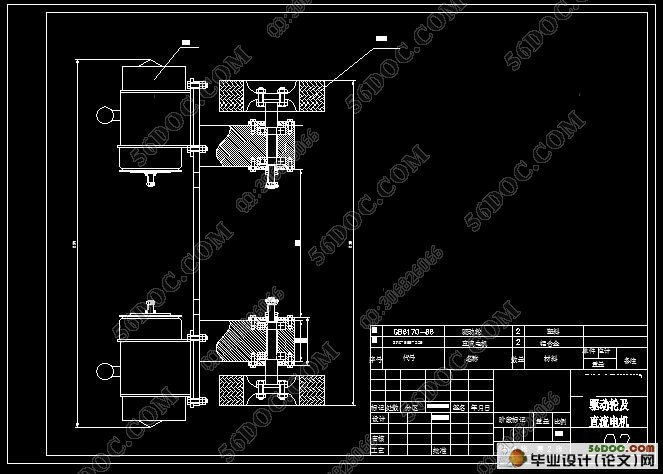
目 录
1 前言••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(2)
2 机构的驱动方案设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(5)
2.1 机器人运动方式的选择••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(5)
2.2 轮式机器人驱动方案设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(9)
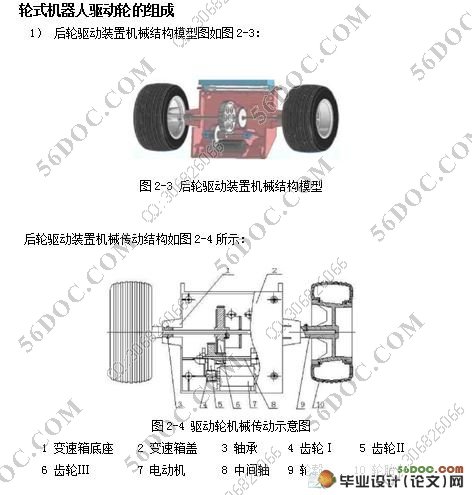
2.2.1轮式机器人驱动轮组成••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(10)
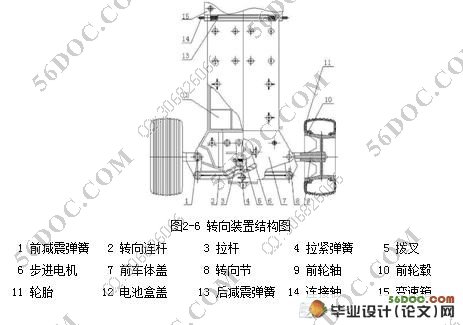
2.2.2轮式机器人转向轮组成••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(11)
2.2.3电机选择••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(12)
2.2.4减速机构的设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(17)
2.2.5变速箱体、前车体及电池箱••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(18)
2.2.6后减震及前减震机构••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(19)
2.2.7车轮和轮毂••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(20)
3 传动机构、执行机构的设计及受力分析••••••••••••••••••••(23)
3.1 传动机构的设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(23)
3.2 执行机构的设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(24)
3.3 机器人受力分析及如何保证加速度最优••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(24)
4 轮式移动机器人的运动学分析••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(26)
4.1 轮式式机器人的运动学建模••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(26)
4.2 阿克曼约束的机器人运动模型••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(29)
5 轮式移动机器人的运动控制系统设计•••••••••••••••••••••••(32)
5.1 控制系统硬件设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(32)
5.2 控制系统软件设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(34)
5.2.2上位机控制系统软件设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(34)
5.2.3下位机控制系统软件设计••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(34)
6 结论••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(36)
参考文献•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(37)
致谢••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••(38)
