城市交通网络的动态路径规划研究
无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
城市交通网络的动态路径规划研究(任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文18000字)
摘要
本文主要结构如下:首先,从供需矛盾的角度对城市道路拥堵现象的成因进行了分析,论证动态路径规划的必要性。然后,以交通系统用户平衡为目标,建立基于METANET宏观交通流模型的动态交通分配优化模型,并用PI反馈分配策略对其进行优化。选取一个复杂交通网络,利用matlab进行仿真,并对结果进行分析。结果表明,合理的交通分配可以均衡交通流、减少交通拥堵。最后,阐述了国内外的路径诱导方法,指出国内路径诱导现存问题、提出建议,对交通路径诱导的前景进行了展望。本文研究的方法对均衡交通流、提高城市交通道路资源利用效率具有重要实际意义。
关键词:用户平衡;反馈分配策略 ;路径诱导;METANET模型
Abstract
This paper is organized as follows: firstly, the cause of traffic congestion is analyzed from the aspect of contradiction between traffic supply and demand, thus the necessity of dynamic route planning is demonstrated. Secondly, taking user equilibrium as an objective function, a dynamic traffic assignment model based on METANET tool is established. The simulation results are presented for a complex traffic network. The simulation and optimization results of matlab indicat that resonable traffic assignment can balance the traffic flow and reduce traffic jam obviously. Lastly, the current route guidance measures are showed. In the meanwhile, several problems for these measures were pointed out. At the end of this paper, it puts forward some suggestions and prospects the future of route guidence. The method used in this paper is significant to balance the traffic flow and improve the efficiency of city traffic network.
Key words: User equilibrium; feedback assignment strategy; route guidance; METANET tool

目 录
摘要 I
第1章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景及意义 1
1.2国内外研究综述 1
1.2.1 国外研究现状 1
1.2.2 国内研究现状 2
1.3、基本内容和技术方案 3
1.3.1 研究基本内容 3
1.3.2技术方案 3
第2章 城市交通拥堵问题形成机理分析 4
2.1城市道路交通需求分析 4
2.2城市道路交通供给分析 5
2.3城市道路交通主体分析 5
第3章 动态路径优化仿真模型构建 7
3.1交通流理论基础 7
3.2经典METANET模型 9
3.2.1 模型基本说明和基本变量 9
3.2.2不区分终点形式的路段模型 9
3.2.3不区分终点形式起点的排队模型 10
3.2.4不区分终点形式起点的节点模型 10
3.2.5区分终点形式的METANET模型 11
3.3动态交通分配模型目标 11
3.3.1 系统最优 12
3.3.2 用户平衡 12
3.4模型优化 13
3.4.1遗传算法 13
3.4.2 反馈分配策略 14
3.5本章小结 14
第4章 对仿真模型进行验证及分析 15
4.1仿真实现设计 15
4.2算例描述 15
4.2.1 交通网络描述 15
4.2.2 交通需求描述 17
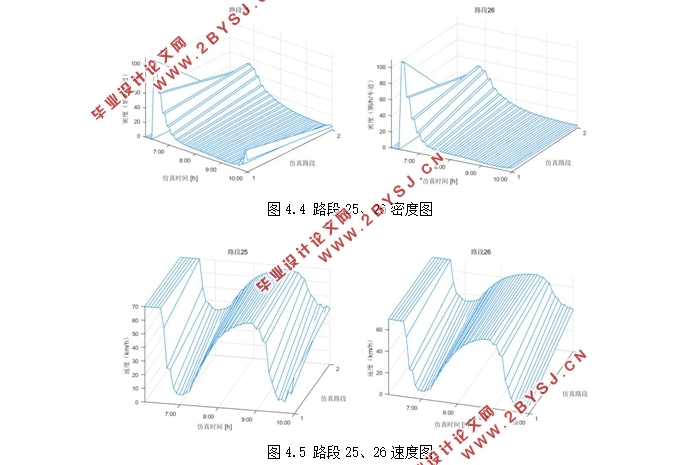
4.3结果分析 17
4.3.1 网络交通状态分析 17
4.3.2 节点分流状态分析 19
第5章 城市交通网络动态路径诱导 21
5.1路径诱导措施 21
5.2我国路径诱导存在的问题 22
5.3路径诱导建议 23
第6章 结论与展望 24
6.1 研究结论 24
6.2研究展望 24
参考文献 26
附录 28
致谢 43
